前言
源码目录说明
硬核源码解析Prometheus系列 :一 、初入Prometheus
- cmd目录是prometheus的入口和promtool规则校验工具的源码
- discovery是prometheus的服务发现模块,主要是scrape targets,其中包含consul, zk, azure, file,aws, dns, gce等目录实现了不同的服务发现逻辑,可以看到静态文件也作为了一种服务发现的方式,毕竟静态文件也是动态发现服务的一种特殊形式
- config用来解析yaml配置文件,其下的testdata目录中有非常丰富的各个配置项的用法和测试
- notifier负责通知管理,规则触发告警后,由这里通知服务发现的告警服务,之下只有一个文件,不需要特别关注
- pkg是内部的依赖
- relabel :根据配置文件中的relabel对指标的label重置处理
- pool:字节池
- timestamp:时间戳
- rulefmt:rule格式的验证
- runtime:获取运行时信息在程序启动时打印
- prompb定义了三种协议,用来处理远程读写的远程存储协议,处理tsdb数据的rpc通信协议,被前两种协议使用的types协议,例如使用es做远程读写,需要远程端实现远程存储协议(grpc),远程端获取到的数据格式来自于types中,就是这么个关系
- promql处理查询用的promql语句的解析
- rules负责告警规则的加载、计算和告警信息通知
- scrape是核心的根据服务发现的targets获取指标存储的模块
- storge处理存储,其中fanout是存储的门面,remote是远程存储,本地存储用的下面一个文件夹
- tsdb时序数据库,用作本地存储
prometheus的启动也可以看作十个不同职能组件的启动。 启动用到了 github.com/oklog 的Group struct, Group collects actors (functions) and runs them concurrently. When one actor (function) returns, all actors are interrupted. 实现多个协程”共进退“的效果(实际上Group 自己也没干啥事儿, 就是封装了业务函数 和 interrupt 两个函数)。
metric scrape 组件
源代码就3个文件
$GOPATH/src/github.com/prometheus/prometheus/scrape
manager.go
scrape.go
target.go
prometheus 示例配置文件
$ cat /usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml
# 全局配置
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # 默认抓取间隔, 15秒向目标抓取一次数据。
evaluation_interval: 15s # 执行rules的频率
alerting:
alertmanagers: ## 配置alertmanager的地址
rule_files:
# - "first.rules"
# - "second.rules"
# controls what resources Prometheus monitors.
scrape_configs:
# 这里是抓取promethues自身的配置
- job_name: 'prometheus'
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
# 重写了全局抓取间隔时间,由15秒重写成5秒。
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']
- job_name: 'mysql'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9104','localhost:9105']
这个配置文件对应 prometheus 的Config struct
type Config struct {
GlobalConfig GlobalConfig `yaml:"global"`
AlertingConfig AlertingConfig `yaml:"alerting,omitempty"`
RuleFiles []string `yaml:"rule_files,omitempty"`
ScrapeConfigs []*ScrapeConfig `yaml:"scrape_configs,omitempty"`
RemoteWriteConfigs []*RemoteWriteConfig `yaml:"remote_write,omitempty"`
RemoteReadConfigs []*RemoteReadConfig `yaml:"remote_read,omitempty"`
// original is the input from which the config was parsed.
original string
}

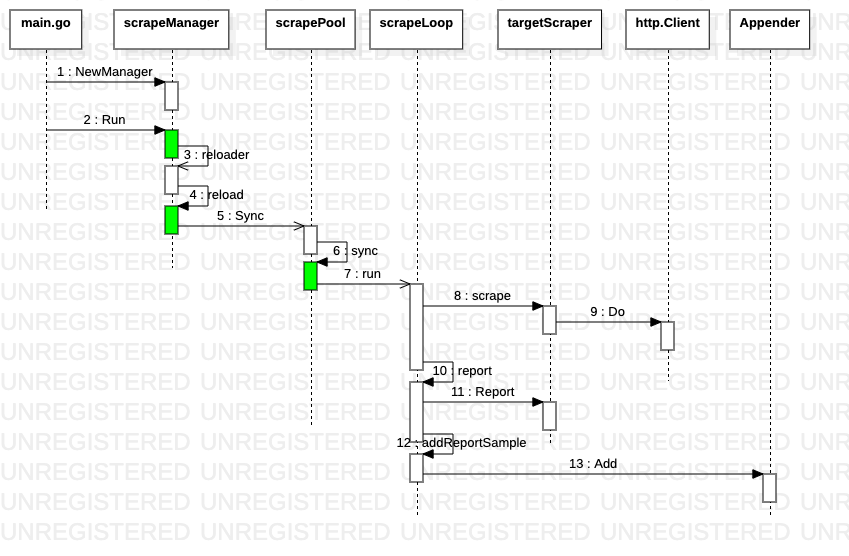
指标服务发现组件discovery 通过channel将最新发现的target传递给scrapeManager err := scrapeManager.Run(discoveryManagerScrape.SyncCh()),scrapeManager服务启动两个协程,一是完成收集指标、存储指标的主要业务逻辑,二是拿到最新target后更新业务逻辑,两个协程的通信也是通过channel(triggerReload chan struct{})
func (m *Manager) Run(tsets <-chan map[string][]*targetgroup.Group) error {
go m.reloader()
for {
select {
case ts := <-tsets:
m.updateTsets(ts)
select {
case m.triggerReload <- struct{}{}:
default:
}
case <-m.graceShut:
return nil
}
}
}
每一个Target 对应一个 ScrapeLoop,ScrapeLoop获取指标后通过append将指标存储到存储组件中,但在中间添加了一层cache层。首先构造存储器和解析器,对指标进行解析,如果不合法就丢弃,否则查看cache中是否存在,根据结果决定是调用AddFast(快速添加)还是Add
Rule Manager
报警规则示例:http status=500 的比例超过2% 时报警
groups:
- name: simulator-alert-rule
rules:
- alert: ErrorRateHigh
expr: sum(rate(http_requests_total{job="http-simulator", status="500"}[5m])) / sum(rate(http_requests_total{job="http-simulator"}[5m])) > 0.02
for: 1m
labels:
severity: major
annotations:
summary: "High Error Rate detected"
description: "Error Rate is above 2% (current value is: "

- rule 分为两种类型:RecordingRule 和 AlertingRule。
- recording rules 是提前设置好一个比较花费大量时间运算或经常运算的表达式,其结果保存成一组新的时间序列数据。当需要查询的时候直接会返回已经计算好的结果,这样会比直接查询快,同时也减轻了PromQl的计算压力,同时对可视化查询的时候也很有用,可视化展示每次只需要刷新重复查询相同的表达式即可。
- 无论是源码还是部署层面,prometheus server 都与alertmanager 平级,prometheus 调用/将报警数据推给alertmanager

prometheus server 提供api 通过PromSQL 获取数据。prometheus Rule Interface 封装了http api的请求与响应。rule.Manager 在此基础上 负责根据rule 发出alert。
// github.com/prometheus/rules/manager.go
type Manager struct {
opts *ManagerOptions
groups map[string]*Group
...
}
type Group struct {
name string
file string
interval time.Duration
rules []Rule
...
}
type Rule interface {
Name() string
Labels() labels.Labels
// 通过http 请求传入 rule,获取符合rule 的metric 数据
Eval(context.Context, time.Time, QueryFunc, *url.URL) (promql.Vector, error)
}
type AlertingRule struct {...}
type RecordingRule struct {...}
