前言
英文文档(如果是外国来的东西),尤其是作者发布的文档,是学习一个东西的最好材料,没有之一。但因为比较精炼,适合学习了足够的背景知识之后再来回顾一下。
摘要
对于摘要部分,用高中做阅读理解的方式来逐字逐句分析 都不过分
- A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. 说明 是一个 去中心化的 electronic cash
- Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. 双花问题是重点
- We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. 给多个交易盖上戳,形成一个记录挂在一个an ongoing chain。记录的生成用到了 proof-of-work,你要改这个记录就得 redoing the proof-of-work
- The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. 交易的确认以最长链为准,最长的链反映了大部分CPU power的意志。
- As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they’ll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. 只有大部分 CPU power 是“善意的”,attacker 就无法一直 控制最长链。==> 一个人无法长久的把持 记账权,那么短期的作假 也就很容易被发现/废弃
- The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone. 节点可以退出和加入,加入时以最长链为准
通过数学、加密算法 等来 制造 工作量,想作恶,得先完成工作量,但一个人不能永远第一快完成工作量,也就不能完全掌握记账权。
对此,我们再来回顾下分布式中的共识问题,2pc/3pc、paxos 等都引入了协调者的角色,然后 数据 以协调者为准。区块链 采用 proof-of-work 的方式 来推选 协调者,谁做的快 以谁为准(也就是充当“协调者”)。但这个协调者 又很短暂,很快就会 易手。
为什么可信
-
no mechanism exists to make payments over a communications channel without a trusted party.
- What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic(用密码写的) proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. 传统的trust based model ==> 中心化的第三方 ==> 不信第三方信密码学
- Transactions that are computationally impractical(不现实的) to reverse would protect sellers from fraud(欺诈)(交易不会被篡改), and routine escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers(交易可以被可信的托管(存储)). 两人不通过第三方直接交易,那么你如何保护sellers?如何保护buyers? 交易一旦达成,即可保证一直存在,不会被篡改。
你用密码写完之后,首先是别人改不了,自己改,得干活儿拿到记账权。
- 传统的trust based model ==> 中心化的第三方 ==> 不信第三方,信密码学 ==> 两人直接交易 ,两人如何取得信任
- 首先是交易一旦达成不能改,信任数学
- 我只和你交易, 我怎么知道你有没有 “一女嫁二夫”==> 你双花可以, 我得知道 ==> 所有的交易全部广播 ==> 所有交易的顺序如何达成一致?==> 每个人都有一个所有交易+顺序的副本,也就是双方知道 彼此 所有的交易记录,也就是你要是把给我的这笔钱 给了别人,我也知道
- 不能改 + 了解对方所有的交易记录 = 信任
- 了解对方/全部的交易记录及其顺序,或者说所有节点取得一致,这才是采用共识机制由来。
那么共识机制算法有很多, paxos虽然复杂点,达成一致也是没问题的,为什么用proof-of-work?
为什么是proof-of-work
The proof-of-work also solves the problem of determining representation in majority decision making. If the majority were based on one-IP-address-one-vote, it could be subverted by anyone able to allocate many IPs. Proof-of-work is essentially one-CPU-one-vote. The majority decision is represented by the longest chain, which has the greatest proof-of-work effort invested in it. 要点:
- one-IP-address-one-vote,无论是paxos、还是2pc/3pc这些,达成共识都是分两步走的,先找到一个基准(协调者),然后取得一致。但如何决定基准,传统共识算法 都是 one-IP-address-one-vote
- one-CPU-one-vote,为了充当协调者(记账权),one-IP-address-one-vote 类算法都是先投票,one-CPU-one-vote 是先干活。they vote with their cpu power
干什么活?中本聪借鉴了 Adam Back’s Hashcash 算法,transactions + prev hash + nonce = hash1, 新的hash 必须包含一定的量的 zero bits(貌似还必须得在最前面)
- attacker 可以改下transaction, 对
transactions + prev hash + nonce重新计算得到hash2, 只要hash2 有一定量的 zero bits 也行,但很明显,hash2 不等于 hash1 - 于是,改了hash2,连带该block 之后所有的block 都得重算
《区块链核心算法解析》 中提到:
- 使用工作量证明机制的首要目的 是调节整个网络 找到区块的速度,使得网络有时间来实现在最新一个区块上的同步。
- 区块链的作用 是维护一个一致的交易历史, 而所有的节点最终都将在 唯一的区块链(交易历史)上达成一致。
- 网络的参与者并非直接决定共识的具体内容,而是通过pow来竞争记账权,间接的达成共识。
tips
本小节,都是一些小点,可以归类到安全机制,也可以说如何节省空间,也可以说比特币发行等,怎么归类都片面的,
激励
- 给旷工发比特币, provides a way to ** initially ** distribute coins into circulation, since there is no central authority to issue them(去中心化影响 货币的方方面面). initially 的含义是:比特币发完之后,旷工就只靠 交易费过活了。
-
The incentive may help encourage nodes to stay honest.If a greedy attacker is able to assemble more CPU power than all the honest nodes
- defraud people by stealing back his payments
- using it to generate new coins
He ought to find it more profitable to play by the rules, such rules that favour him with more new coins than everyone else combined, than to undermine the system and the validity of his own wealth. 欺诈用户的事儿干多了,人们将不再信任比特币系统,attacker欺诈省掉的/拿到的比特币也就不值钱了。attacker 如果有这个计算资源,与其搞破坏,不如老老实实挖矿赚钱。
-
根据merkle tree 的一些特性,底层数据的任何变动都会传导到父节点,最终传导到 根节点。根的值实际代表了 对底层所有数据的 “数字摘要”。所以,对于block-chain 中比较早的 block来说,交易数据可以discard(如果你不关心所有人的所有交易链路的话)。A block header with no transactions would be about 80 bytes. If we suppose blocks are generated every 10 minutes, 80 bytes * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB per year. 全放内存都没有关系。
-
It is possible to verify payments without running a full network node. A user only needs to keep a copy of the block headers of the longest proof-of-work chain,He can’t check the transaction for himself, but by linking it to a place in the chain, he can see that a network node has accepted it. 轻钱包,交易本身合不合法无法直接确认(因为无法直接校验交易的输入 等),但可以向节点查询交易是否在 最长链中。
-
SPV, 简单支付验证(SPV)与创新 交易确认与支付确认,有的文章对着两个概念不作区别,经常混淆使用。区块链如何运用merkle tree验证交易真实性 要点如下:
- Merkle Tree, 把merkle root保存在区块头中,交易数据被保存在区块体中,Merkle Tree中间当那些hash并没有被保存,它们只是运算过程数据。Merkle Tree 还被用于p2p 下载时的文件校验
-
merkle block message(spv 发出的请求 ) 和 验证路径 (节点对 spv 请求的响应)
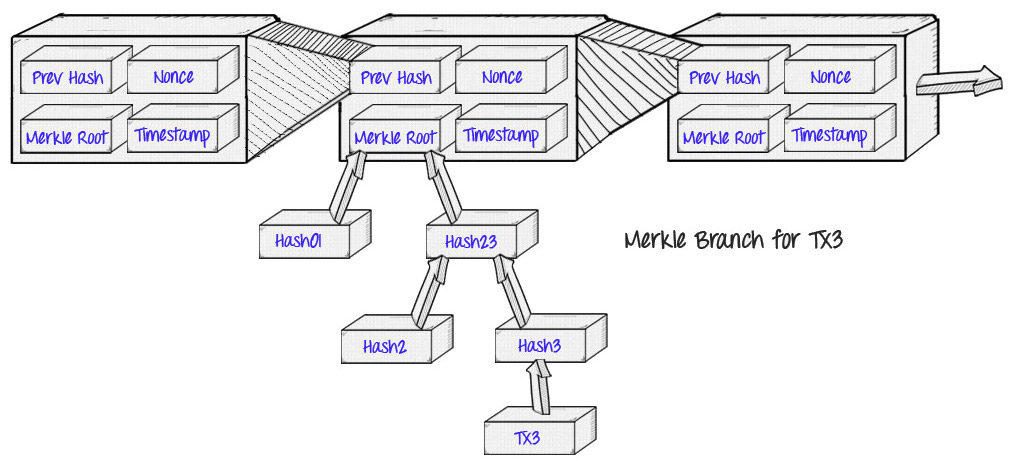
- 节点 如何 根据交易信息 得到交易所在的block,并返回 验证路径
- spv 如何 确认 验证路径 是否正确。 同步最长区块链 ==> 确认merkle root在最长链中 ==> merkle root 可信 ==> spv 根据返回 验证路径(hash01,hash23,hash2,hash3,hash(tx3)) 重新计算merkle root ==> 验证路径真实 ==> 交易已被最长链确认
-
a new key pair should be used for each transaction to keep them from being linked to a common owner. 每个交易 都有一个new key pair
- 掩盖owner 的身份
- bitcoin 的接收者 在 交易快开始时 才将 key pair 给sender,防止 sender 提前 算好交易数据,提高了sender 拿到记账权的可能性
conclusion
适合多次重复读
We have proposed a system for electronic transactions without relying on trust(这句是纲领). We started with the usual framework of coins made from digital signatures, which provides strong control of ownership, but is incomplete without a way to prevent double-spending. To solve this, we proposed a peer-to-peer network using proof-of-work to record a public history of transactions that quickly becomes computationally impractical for an attacker to change if honest nodes control a majority of CPU power. The network is robust in its unstructured simplicity. Nodes work all at once with little coordination. They do not need to be identified, since messages are not routed to any particular place and only need to be delivered on a best effort basis. Nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone. They vote with their CPU power, expressing their acceptance of valid blocks by working on extending them and rejecting invalid blocks by refusing to work on them. Any needed rules and incentives can be enforced with this consensus mechanism.
- digital signatures,解决隐私和不可篡改性
- peer-to-peer network using proof-of-work 解决双花问题
- Nodes work all at once with little coordination,do not need to be identified,vote with their CPU power
- other rules and incentives can be enforced with this consensus mechanism.
