简介
Zookeeper is a distributed storage that provides the following guarantees
- Sequential Consistency - Updates from a client will be applied in the order that they were sent.
- Atomicity - Updates either succeed or fail. No partial results.
- Single System Image - A client will see the same view of the service regardless of the server that it connects to.
- Reliability - Once an update has been applied, it will persist from that time forward until a client overwrites the update.
- Timeliness - The clients view of the system is guaranteed to be up-to-date within a certain time bound.
You can use these to implement different recipes that are required for cluster management like locks, leader election etc.
从这段描述中,我们就可以知道,什么是本质(distributed storage + guarantees),什么是recipes。
2017.11.23 更新
我们都以为用zookeeper做一致性工具天经地义,来自京东、唯品会对微服务编排、API网关、持续集成的实践分享(上)却用db做一致性,一切看场景。就注册中心的功能来说,Netflix/eureka也比zookeeper更好些。换个方式考虑,注册中心本质为了服务调用方和提供方的解耦,存储服务注册信息。也就是能存数据的都可以用来做注册中心,但从可用性上考虑,zookeeper因为副本因素可靠性高些。一致性 <== 副本 <== 高可用性存储,这或许才是zookeeper等一致性工具的本质,其它的才是kv存储、通知机制等枝节。
现有产品
分布式配置系统一般有zookeeper,etcd,Consul,Eureka(AP)等
分布式配置中心一般有以下特点:
- 集中管理外部依赖的服务配置和服务内部配置
- 提供web管理平台进行配置和查询
- 支持服务注册与发现
- 支持客户端拉取配置
-
支持订阅与发布,配置变更主动通知到client,实时变更配置
这条跟消息队列很像,不过两者的目的完全不同。
-
分布式配置中心本身具有非常高的可靠性
因此一般以集群状态运行,集群节点的增加和减少不影响服务的提供。
我个人觉得比较直观的一条便是:
- 使用之前,分布式系统各主机间交互,需要跨网络访问
-
使用之后,分布式系统的daemon服务只需与配置中心daemon交互即可。省事,尤其是一个消息要通知好几个主机时。
- 两台电脑互通,需要一根网线
- 三台电脑互通,需要三根网线
- 四台电脑互通,需要六根网线
- 四台电脑互通,如果使用集线器,则需要四根网线即可
其作用类似于集线器,不同主机的各个进程连上它,就不用彼此之间费事通信了,当然,通信的数据一般是对连接上配置中心的所有进程都有用的。如果是交互的数据量太大,或数据只与某两个进程相关,还是各主机自己动手或使用消息队列。
通过安装过程来体会工具的异同
etcd
深入剖析数据多版本 MVCC 机制tcd 虽然有很多丰富的功能,也有它特殊的定位,但本质上也是一个存储系统。存储系统核心功能其实非常简单,聚焦三个操作:读写删。不过 etcd 有两个特色的功能:watch 机制和 MVCC 机制( 数据多版本 )。MVCC 带来了什么?可靠的 watch 机制;简单的事务并发控制。这两点其实非常容易理解,一个 key 的历史版本全部被记录,而不是覆盖更新,那这个对于 watch 就太友好了。毕竟历史都在这嘛,数据又安全读出来又方便。MVCC 的设计中,可以认为用户的删除都是标记删除,真正回收由一个叫做 compact 的操作来实现。
etcd原理剖析 写的非常好。
以ubuntu15.04 为例,用Systemd管理etcd,针对每个主机
- 下载文件
https://github.com/coreos/etcd/releases - 拷贝可执行文件etcd,etcdctl到path目录
-
准备
/etc/systemd/system/etcd.service文件[Unit] Description=etcd shared configuration and service discovery daemon [Service] Type=notify EnvironmentFile=/etc/default/etcd ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/etcd $ETCD_OPTS Restart=on-failure RestartSec=5 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target -
准备配置文件
/etc/default/etcdETCD_OPTS=-addr=server_ip:4001 -peer-addr=server_ip:7001 -data-dir=/var/lib/etcd/ systemctl enable etcd使配置文件生效,systemctl start etcd启动etcd,systemctl status etcd查看etcd运行状态。
几个端口的作用
- 4001,客户端(比如使用etcd的应用程序)通过它访问etcd数据
- 7001,Etcd节点通过7001端口在集群各节点间同步Raft状态和数据
etcd启动时,有三种模式static,etcd Discovery和DNS Discovery三种模式来确定哪些节点是“自己人”,参见https://coreos.com/etcd/docs/latest/clustering.html
存储结构,键值对,键以文件夹的形式组织,例如
root@docker1:~# etcdctl ls /network/docker/nodes
/network/docker/nodes/192.168.56.101:2375
/network/docker/nodes/192.168.56.102:2375
CP/zookeeper
针对每个主机
- 将文件解压到特定位置,
tar -xzvf zookeeper-x.x.x.tar.gz -C xxx - 根据样本文件创建配置文件,
cp zookeeper-x.x.x/zoo_sample.cfg zookeeper-x.x.x/zoo.cfg -
更改配置文件
dataDir=/var/lib/zookeeper clientPort=2181 server.1=server_ip1:2888:3888 server.2=server_ip2:2888:3888 server.3=server_ip3:2888:3888 - 编辑myid文件,
${dataDir}/myid,不同的节点写个不同的数字即可 - 启动zookeeper,
zookeeper-x.x.x/bin/zkServer.sh start
几个端口的作用:
- 端口2181由 ZooKeeper客户端(比如访问zookeeper数据的应用程序)使用,用于连接到 ZooKeeper 服务器;
- 端口2888由对等 ZooKeeper 服务器使用,用于互相通信;
- 而端口3888用于领导者选举。
集群配置时,集群有哪些节点,已在所有节点的配置文件中讲明,比如这里的server.1,server.2,server.3
因为大数据系统通常都是主从架构,主服务器管理集群的状态和元信息(meta-info),为了保证集群状态一致防止“脑裂”,所以运行期只能有一个主服务器工作(active master),但是为了保证高可用,必须有另一个主服务器保持热备(standby master)。那么应用程序和集群其他服务器如何才能知道当前哪个服务器是实际工作的主服务器呢?所以很多大数据系统都依赖 ZooKeeper 提供的一致性数据服务,用于选举集群当前工作的主服务器。一台主服务器启动后向 ZooKeeper 注册自己为当前工作的主服务器,而另一台服务器就只能成为热备主服务器,应用程序运行期都和当前工作的主服务器通信。如果当前工作的主服务器宕机(在 ZooKeeper 上记录的心跳数据不再更新),热备主服务器通过 ZooKeeper 的监控机制发现当前工作的主服务器宕机,就向 ZooKeeper 注册自己成为当前工作的主服务器。应用程序和集群其他服务器跟新的主服务器通信,保证系统正常运行。
consul
因为consul 是新近流行的,所以专门介绍一下
Consul 和其它配置中心通用的一些特性
- Service Discovery,比较有特色的是支持dns 或http interface
- Key/Value Storage - A flexible key/value store enables storing dynamic configuration, feature flagging, coordination, leader election and more. The simple HTTP API makes it easy to use anywhere.
Consul 独有支持的一些特性
- Health Checking - Health Checking enables Consul to quickly alert operators about any issues in a cluster. The integration with service discovery prevents routing traffic to unhealthy hosts and enables service level circuit breakers. 没有HealthCheck时,zk 一般通过心跳做简单判断
- Multi-Datacenter - Consul is built to be datacenter aware, and can support any number of regions without complex configuration.
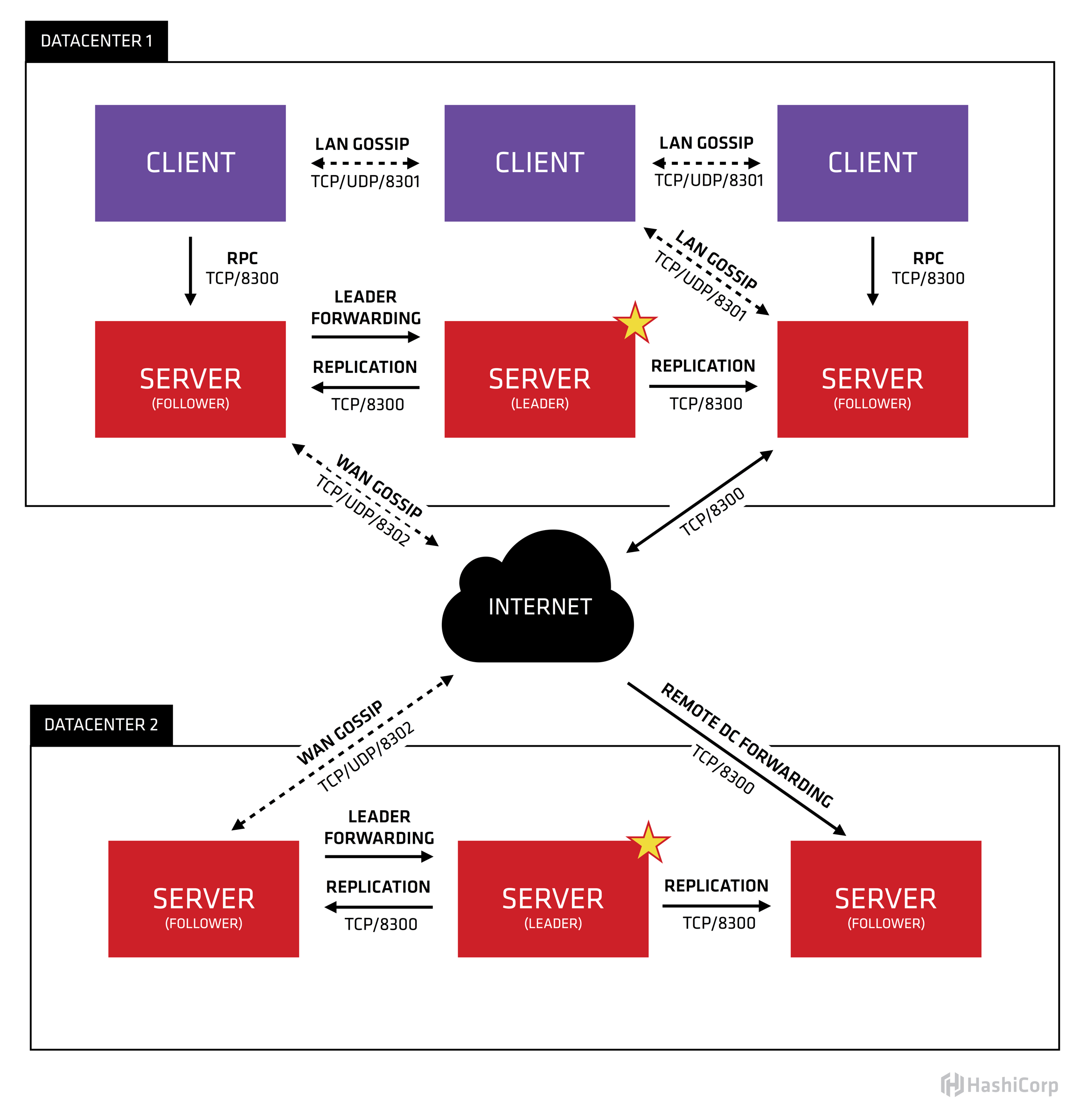
consul 两个角色:server,client(都叫consul agent)。 先说server 的安装,假设存在192.168.60.100,192.168.60.101,192.168.60.102 三个节点
nohup consul agent -server -bootstrap -syslog \ ## -bootstrap 只需一个节点即可
-ui-dir=/opt/consul/web \
-data-dir=/opt/consul/data \
-config-dir=/opt/consul/conf \
-pid-file=/opt/consul/run/consul.pid \
-client='127.0.0.1 192.168.60.100' \
-bind=192.168.60.100 \
-node=192.168.60.100 2>&1 &
每个server 节点相机改下 ip地址即可。
当一个Consul agent启动后,它并不知道其它节点的存在,它是一个孤立的单节点集群。它必须加入到一个现存的集群来感知到其它节点的存在。
consul join --http-addr 192.168.60.100:8500 192.168.60.101
consul join --http-addr 192.168.60.100:8500 192.168.60.102
然后执行 consul member 即可列出当前的集群状态。
Consul默认是在前台运行的,所以使用systemd 来启动和consul 是最佳方案。
/etc/systemd/system/consul.service
[Unit]
Description=Consul service discovery agent
Requires=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
#User=consul
#Group=consul
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/consul
Environment=GOMAXPROCS=2
Restart=on-failure
#ExecStartPre=[ -f "/opt/consul/run/consul.pid" ] && /usr/bin/rm -f /opt/consul/run/consul.pid
ExecStartPre=-/usr/local/bin/consul configtest -config-dir=/opt/consul/conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/consul agent $CONSUL_OPTS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillSignal=SIGTERM
TimeoutStopSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
/etc/default/consul
CONSUL_OPTS=”-server -syslog -data-dir=/opt/consul/data -config-dir=/opt/consul/conf -pid-file=/opt/consul/run/consul.pid -client=0.0.0.0 -bind=192.168.60.100 -join=192.168.60.100 -node=192.168.60.100”
为什么要有一个 consul client?
- 因为除了consul server外,consul 推荐数据中心所有的节点上部署 consul client ,这样所有的服务只需与本地的consul client 交互即可,业务本身无需感知 consul server 的存在。PS: 有点service mesh的意思
- consul 的一个重要特性是健康检查,就像Kubernetes 一样 可以为容器注册一个readinessProbe,如果让有限数量的consul server 去执行数据中心成百上千服务的healthcheck,负担就太大了。
consul 启动时,默认有一个-dc 参数,默认是dc1。
nacos
nacos下载地址 下载可执行文件解压
nacos-server-$version
bin
shutdown.cmd
shutdown.sh
startup.cmd
startup.sh
conf
application.properties
application.properties.example
cluster.conf.example
target
nacos-server.jar
单机模式启动sh startup.sh -m standalone
集群模式下,应先设置配置文件 cluster.conf
# ip:port
200.8.9.16:8848
200.8.9.17:8848
200.8.9.18:8848
数据模型
zookeeper
ZooKeeper的数据结构, 与普通的文件系统类似,每个节点称为一个znode. 每个znode由3部分组成:
- stat. 此为状态信息, 描述该znode的版本, 权限等信息.
- data. 与该znode关联的数据.
- children. 该znode下的子节点.
consul
Consul做服务发现是专业的,配置管理更像是捎带的
- node 管理,所有的分布式系统都需要 node 管理
-
有专门的服务管理:Service 有专门的数据对象、页面UI入口,专门的注册与查询接口
{ "services": [ { "id": "hello1", "name": "hello", "tags": [ "primary" ], "address": "172.17.0.5", "port": 5000, "checks": [ { "http": "http://localhost:5000/", "tls_skip_verify": false, "method": "Get", "interval": "10s", "timeout": "1s" } ] } ] } - 健康检查是其中一项必不可少的功能
- Consul提供了一个易用的键/值存储,可以用来保持动态配置,协助服务协调,领袖选举等。
nacos
//Config Service Interface
public interface ConfigService {
String getConfig(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException;
String getConfigAndSignListener(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs, Listener listener) throws NacosException;
void addListener(String dataId, String group, Listener listener) throws NacosException;
boolean publishConfig(String dataId, String group, String content) throws NacosException;
boolean removeConfig(String dataId, String group) throws NacosException;
void removeListener(String dataId, String group, Listener listener);
String getServerStatus();
}
服务模型
consul/nacos等中间件被分成了两块功能:服务注册发现(Naming)和配置中心(Config)。一般在聊注册中心时,都会以 Zookeeper 为引子,这也是很多人最熟悉的注册中心。但如果你真的写过或看过使用 Zookeeper 作为注册中心的适配代码,会发现并不是那么容易,再加上注册中心涉及到的一致性原理,这就导致很多人对注册中心的第一印象是:这个东西好难!但归根到底是因为 Zookeeper 根本不是专门为注册中心而设计的,其提供的 API 以及内核设计,并没有预留出「服务模型」的概念,这就使得开发者需要自行设计一个模型,去填补 Zookeeper 和服务发现之间的鸿沟。微服务架构逐渐深入人心后,Nacos、Consul、Eureka 等注册中心组件进入大众的视线。可以发现,这些“真正”的注册中心都有各自的「服务模型」,在使用上也更加的方便。
- 服务注册,registerInstance/registerService
- 服务隔离,namespace/group/cluster
- 服务发现
- 推模型,subscribe/unsubscribe
- 拉模型,getAllInstances/selectInstances
nacos
Nacos 概念相关概念
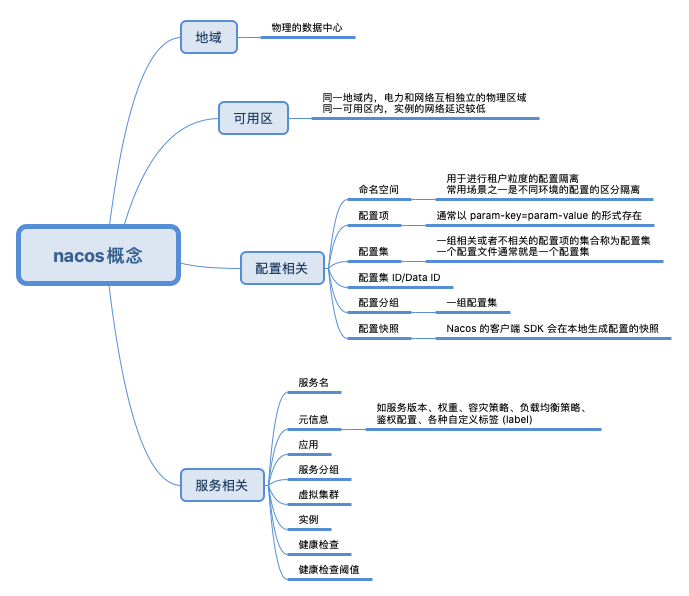
- 健康检查,以指定方式检查服务下挂载的实例 (Instance) 的健康度,从而确认该实例 (Instance) 是否能提供服务。
- 健康保护阈值,为了防止因过多实例 (Instance) 不健康导致流量全部流向健康实例 (Instance) ,继而造成流量压力把健康 健康实例 (Instance) 压垮并形成雪崩效应,应将健康保护阈值定义为一个 0 到 1 之间的浮点数。当域名健康实例 (Instance) 占总服务实例 (Instance) 的比例小于该值时,无论实例 (Instance) 是否健康,都会将这个实例 (Instance) 返回给客户端。这样做虽然损失了一部分流量,但是保证了集群的剩余健康实例 (Instance) 能正常工作。
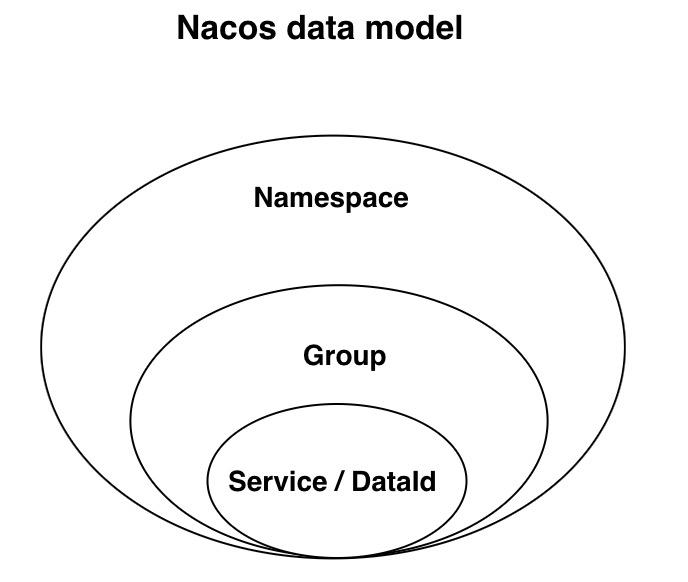
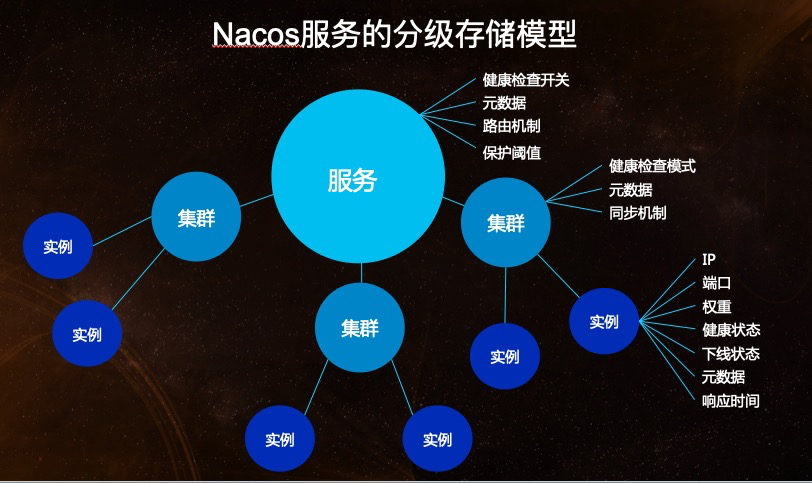
nacos 对外提供http api,下文进一步通过java client sdk 演示 与nacos server的互动
//服务发现注册接口
public interface NamingService {
void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, String ip, int port, String clusterName) throws NacosException;
void deregisterInstance(String serviceName, String ip, int port) throws NacosException;
List<Instance> getAllInstances(String serviceName, String groupName) throws NacosException;
List<Instance> selectInstances(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters, boolean healthy, boolean subscribe) throws NacosException;
Instance selectOneHealthyInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters, boolean subscribe) throws NacosException;
void subscribe(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters, EventListener listener) throws NacosException;
void unsubscribe(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters, EventListener listener) throws NacosException;
ListView<String> getServicesOfServer(int pageNo, int pageSize, String groupName, AbstractSelector selector) throws NacosException;
List<ServiceInfo> getSubscribeServices() throws NacosException;
String getServerStatus();
}
我们使用zk 做服务注册中心时,对zk 的api 和服务发现注册操作 之间要进行一些语义转换,NamingService 接口定义了 服务发现注册的 api。
NamingService 使用demo
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("serverAddr", System.getProperty("serverAddr"));
properties.setProperty("namespace", System.getProperty("namespace"));
NamingService naming = NamingFactory.createNamingService(properties);
naming.registerInstance("nacos.test.3", "11.11.11.11", 8888, "TEST1");
ConfigService 使用demo
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("serverAddr", serverAddr);
ConfigService configService = NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties);
String content = configService.getConfig(dataId, group, 5000);
服务注册中心
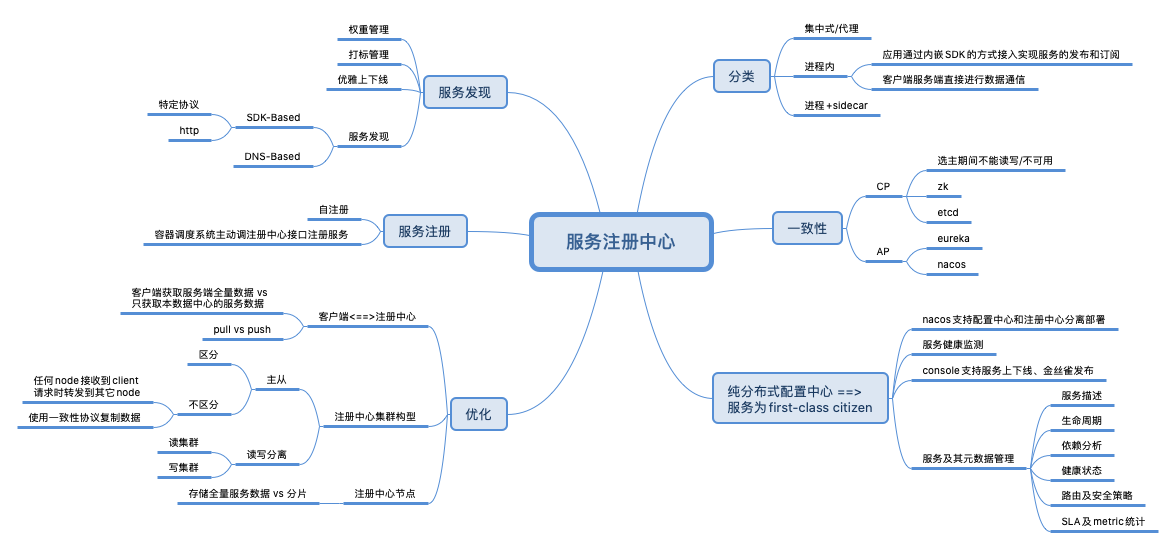
| 健康监测实现 | |
|---|---|
| zookeeper | 利用临时节点的机制,业务服务启动时创建临时节点,节点在服务就在,节点不存在服务就不存在 |
| etcd | 利用TTL机制,业务服务启动时创建键值对,定时更新ttl,ttl过期则服务不可用 |
| consul | consul agent每个node一个,会所在节点的服务进行健康检查 |
ZooKeeper、etcd通过键值存储来实现服务的注册与发现,键值存储都是强一致性的,也就是说键值对会自动同步到多个节点,只要在某个节点上存在就可以认为对应的业务服务是可用的。
小结
分布式配置系统一般有以下不同:
- 对外提供的数据格式未完待续
- 一致性原理
有以下相同的地方
- 都会将部分数据存储在本地(可指定存储目录)
- 都是master-slave机制,当master挂掉时,集群立即协商新的master,并以master为准同步数据。
- 分布式配置中心为提高可靠性,会以集群的形态存在,那么集群在启动时,如何判定哪些节点是“自己人”。
其它,随着版本的发展,etcd和zookeeper等配置项和端口的意义会有些变化,此处不再赘述。
