前言
envoy 好在哪里?
动态性:Envoy 的配置高度依赖接口自动化产生各种配置,这些配置是可以进行 Runtime 修改而无需 reload 文件,在现代应用架构中,一个服务端点的生命周期都变得更短,其运行的不确定性或弹性都变得更大,所以能够对配置进行 runtime 修改而无需重新 reload 配置文件这个能力在现代应用架构中显得尤其珍贵,这正是 Istio 选择 Envoy 作为数据平面的一个重要考虑。Envoy 同时还具备热重启能力,这使得在升级或必须进行重启的时候变得更加优雅,已有连接能够得到更多的保护。
扩展性:Envoy 的配置中可以看到大量的 filter,这些都是其扩展性的表现,Envoy 学习了 F5 以及 NGINX 的架构,大量使用插件式,使得开发者可以更加容易的开发。从 listener 开始就支持使用 filter,支持开发者开发 L3,L4,L7 的插件从而实现对协议扩展与更多控制。
可观测性:可观测的三大组件:logs,metrics,tracing 默认都被 Envoy 所支持。Envoy 容许用户以灵活的方式在灵活的位置定义灵活的日志格式,这些变化可以通过动态配置下发从而实现立即生效,并容许定义对日志的采样等。在 Metrics 则提供了能够与 Prometheus 进行集成的诸多指标,值得一提的是 Envoy 容许 filter 本身来扩充这些指标,例如在限流或者验证等 filter 中容许插件本身定义属于自己的指标从而帮助用户更好的使用和量化插件的运行状态。在 Tracing 方面 Envoy 支持向 zipkin,jaeger,datadog,lightStep 等第三方集成,Envoy 能够生产统一的请求 ID 并在整个网络结构中保持传播,同时也支持外部的 x-client-trace-id,从而实现对微服务之间关系拓扑的描述。
流量管理配置
Envoy 基于文件的动态配置 Envoy 基于 API 的动态配置 未读
功能划分
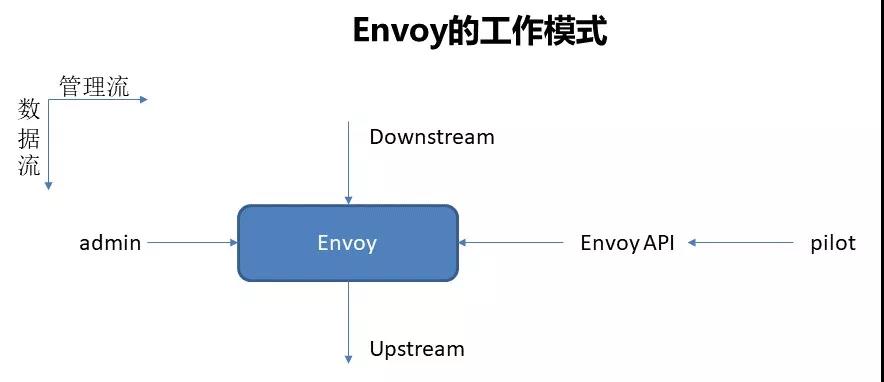
Envoy的工作模式如图所示,横向是管理平面/管理流,纵向是数据流。Envoy会暴露admin的API,可以通过API查看Envoy中的路由或者集群的配置。
Envoy按照使用 场景可以分三种:
- sidecar,和应用一起部署在容器中,对进出应用服务的容量进行拦截
- router,作为独立的代理服务,对应用的L4/L7层流量进行代理
- ingress,作为集群入口的Ingress代理,对集群的入口流量进行拦截和代理
router 和ingress 均属于和应用服务不在一起的纯代理场景,可以归为一类,成为Gateway模式。对于sidecar 模式来说, envoy 负责服务出入方向流量的透明拦截,并且出入方向的流量在监听管理、路由管理等方面有很大的区别,因此sidecar 的xds配置是按照出入方向分别进行组织和管理。因此从xds 配置的视角上 配置可以划分为
- sidecar inbound,inbound 将发往本节点的流量转发到 对应的服务节点,因此inbound 方向的集群和路由信息都比较确定:单一的集群,单一的VirtualHost,并且集群固定只有一个节点信息。对于Http来说,会拼装HTTP 对应的路由信息,对于TCP来说,直接通过Tcp Proxy方式进行路由,只做全局统计和管控,无法进行协议相关的链路治理。
- sidecar outbound,从当前节点发往节点外的流量。根据协议的不同有所不同,待进一步认识。
- gateway
envoy sidecar 配置 与 xds
Envoy是一个高性能的C++写的proxy转发器,那Envoy如何转发请求呢?需要定一些规则,然后按照这些规则进行转发。规则可以是静态的,放在配置文件中的,启动的时候加载,要想重新加载,一般需要重新启动。当然最好的方式是规则设置为动态的,放在统一的地方维护,这个统一的地方在Envoy眼中看来称为Discovery Service,Envoy过一段时间去这里拿一下配置,就修改了转发策略。无论是静态的,还是动态的,在配置里面往往会配置四个东西。
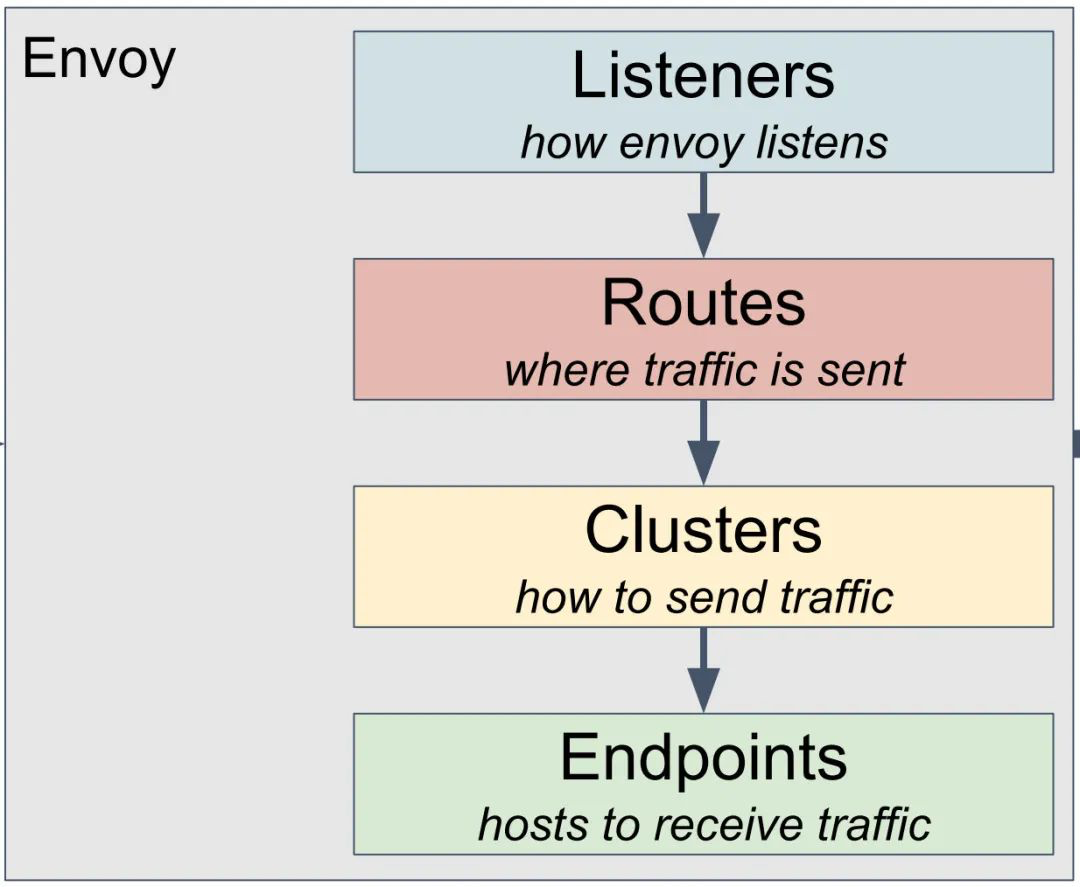
| xds | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|
| Listener | LDS | 既然是proxy,就得监听一个端口 |
| Endpoints | EDS | 目标的ip地址和端口,这个是proxy最终将请求转发到的地方 |
| Routes | RDS | 一个cluster是具有完全相同行为的多个endpoint 它们组成一个Cluster,从cluster到endpoint的过程称为负载均衡 |
| Cluters | CDS | 有时候多个cluster具有类似的功能,但是是不同的版本号, 可以通过route规则,选择将请求路由到某一个版本号 |

| envoy | nginx | |
|---|---|---|
| 监听入口 | listener | listener 以及部分 Server 段落配置 |
| 路由控制逻辑 | route | 各种 Locations 匹配等 |
| clusters | upstream | |
| endpoints | upstream 里的 server |
envoy ingress 配置 与xds
istio 的流控支持那么多功能,由用户直接 决定 给某个pod 的envoy 发送 xds 数据是不现实的。Traffic ManagementYou can do all this and more by adding your own traffic configuration to Istio using Istio’s traffic management API.
| 流量管理 | traffic management API |
|---|---|
| traffic routing | VirtualService + DestinationRule |
| Timeouts | VirtualService.spec.http.timeout |
| Retries | VirtualService.spec.http.retries |
| Circuit breakers | DestinationRule.spec.trafficPolicy |
| Fault injection | VirtualService.spec.http.fault |
- With a virtual service, you can specify traffic behavior for one or more hostnames. You use routing rules in the virtual service that tell Envoy how to send the virtual service’s traffic to appropriate destinations.
- You can think of virtual services as how you route your traffic to a given destination, and then you use destination rules to configure what happens to traffic for that destination.
- Gateway configurations are applied to standalone Envoy proxies that are running at the edge of the mesh, rather than sidecar Envoy proxies running alongside your service workloads. Istio’s Gateway resource just lets you configure layer 4-6 load balancing properties such as ports to expose, TLS settings, and so on. Then instead of adding application-layer traffic routing (L7) to the same API resource, you bind a regular Istio virtual service to the gateway. This lets you basically manage gateway traffic like any other data plane traffic in an Istio mesh. Gateway 负责4~6层,与其绑定的VirtualService 负责七层,管理gateway就像管理普通的数据面代理一样。
流量管理
一个istio 自带的Bookinfo 为例,对应istio-1.4.2-linux.tar.gz 解压后istio-1.4.2/samples/bookinfo
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
# 安装 bookinfo 的 ingress gateway:
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
全流程都是 http 协议
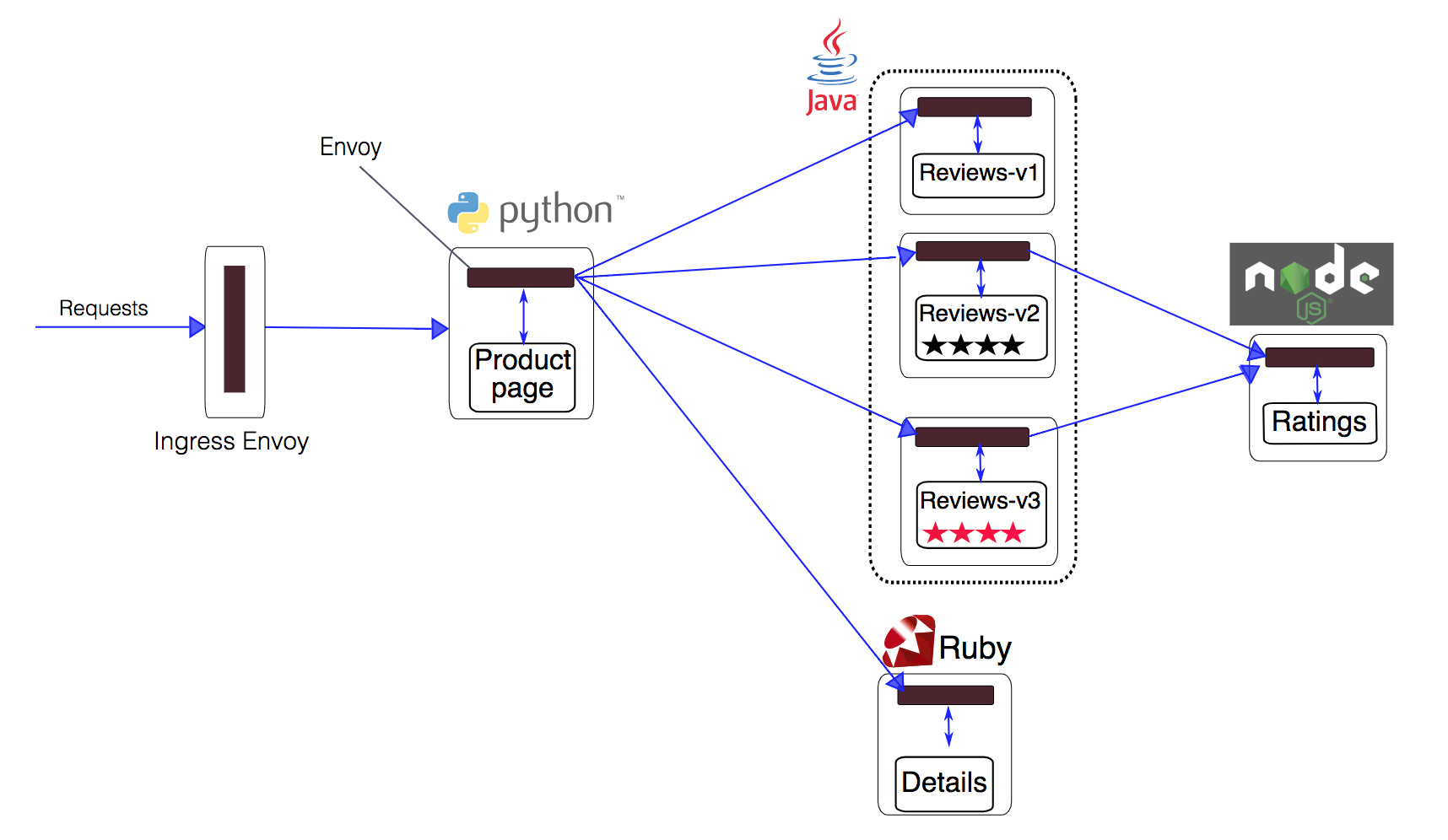
下文 大部分时候 以bookinfo 为例
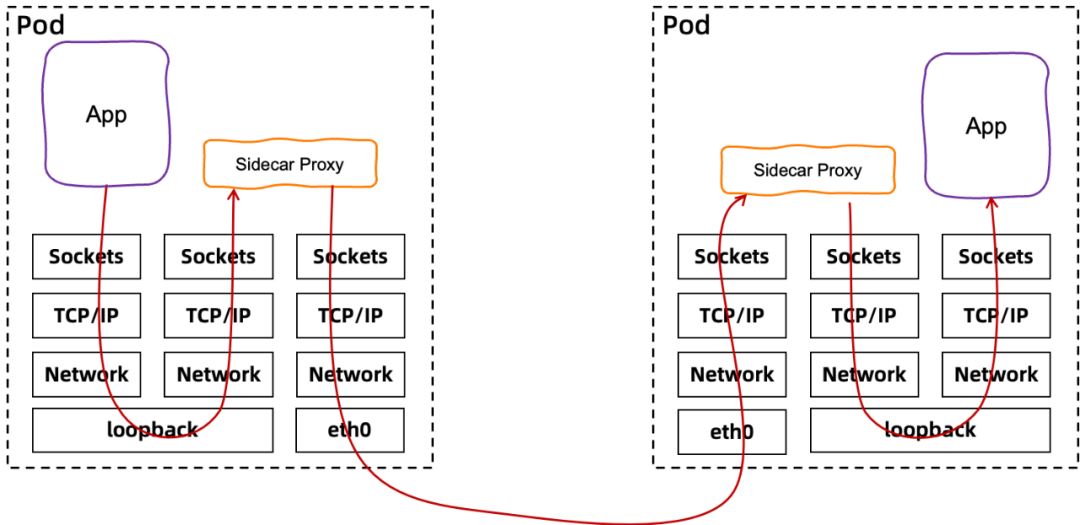
Pod内流量 管理
流量拦截
深入解读Service Mesh背后的技术细节istio 对流量采取了透明拦截的方式
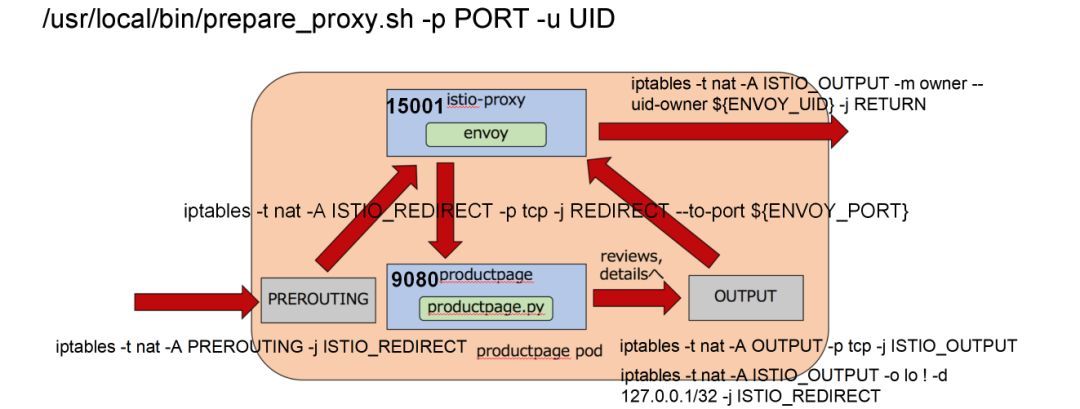
- 在PREROUTING规则中,使用这个转发链,从而进入容器的所有流量,都被先转发到envoy的15000端口。
- envoy作为一个代理,已经被配置好了,将请求转发给productpage程序。
- productpage程序接受到请求,会转向调用外部的reviews或者ratings,当productpage往后端进行调用的时候,就碰到了output链,这个链会使用转发链,将所有出容器的请求都转发到envoy的15000端口。这样无论是入口的流量,还是出口的流量,全部用envoy做成了汉堡包。
- envoy根据服务发现的配置,知道reviews或者ratings如何访问,于是做最终的对外调用。iptables规则会对从envoy出去的流量做一个特殊处理,允许他发出去,不再使用上面的output规则。
目标端口被改写后, 可以通过SO_ORIGINAL_DST TCP 套件获取原始的ipport
envoy 内部流转
envoy 是一个proxy 组件,一个proxy 具体的说是listener、filter、route、cluster、endpoint 的协同工作
为了实现正确的流量路由与转发,envoy 的监听器分为两类
- 虚拟监听器,需要绑定相应的端口号,iptables 拦截的流量会转发到这个端口上
- 真实监听器,用于处理iptables 拦截前的”真实目的地址“,虚拟机监听器接收到监听请求时,按照一定的匹配规则找到对应的真实监听器进行处理。真实监听器因为不需要和网络交互,因此不需要配置和绑定端口号。
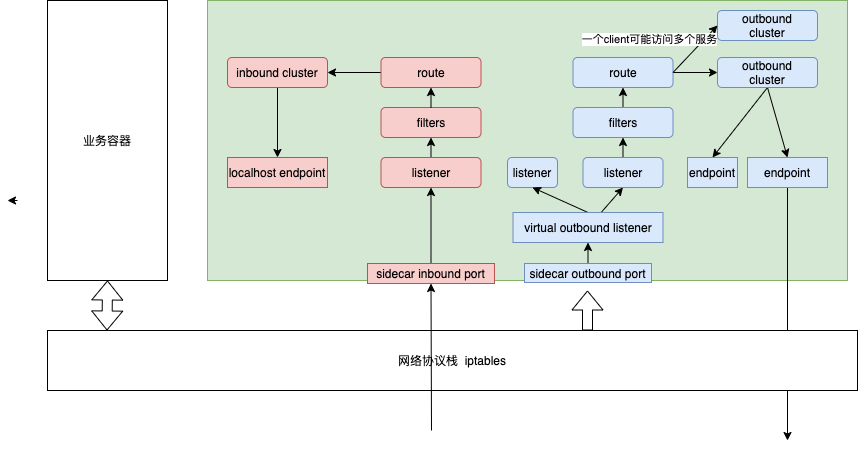
理解 Istio Service Mesh 中 Envoy Sidecar 代理的路由转发 未读
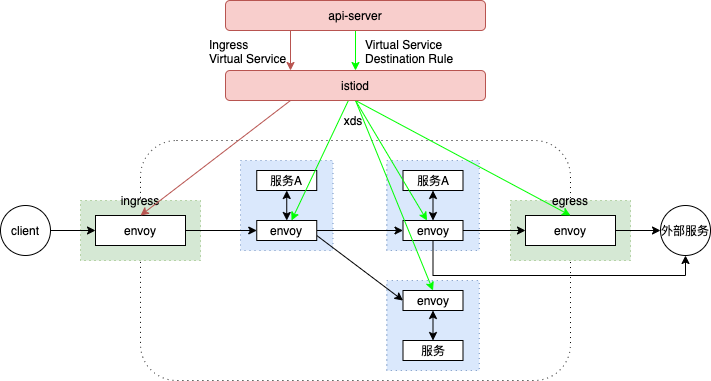
网格内流量管理
istioctl proxy-config listener $podname 可以查看Pod 中的具有哪些 Listener,也可以使用istioctl proxy-config listener $podname -o json 查看更详细的配置
Istio流量管理实现机制深度解析Productpage服务调用Reviews服务的请求流程
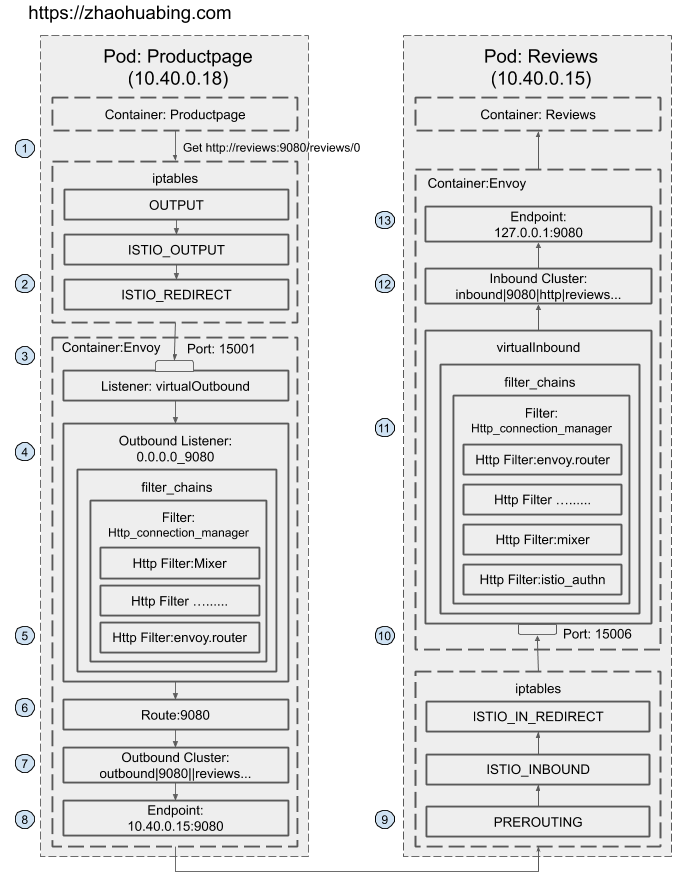
将details 服务扩容到2个实例,可以通过Pilot的调试接口获取该Cluster的endpointhttp://pilot_service_ip:15014/debug/edsz ,可以看到 details 对应的cluster的endpoints 变成了两个。查看 productpage pod中 envoy 的endpoint 配置发现也对应有了2个endpoint
$ istioctl pc endpoint productpage-v1-596598f447-nn64q
ENDPOINT STATUS OUTLIER CHECK CLUSTER
10.20.0.10:9080 HEALTHY OK outbound|9080||details.default.svc.cluster.local
10.20.0.2:9080 HEALTHY OK outbound|9080||details.default.svc.cluster.local
进出网格的流量管理
Exploring Istio - The VirtualService resource 整体来说,istio Virtual Service 更像k8s Ingress
| k8s Service | k8s Ingress | istio Virtual Service | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 流量导给谁 | Pod | Service | Service Pod |
| 路由规则 | 权重 | host and path path匹配语法的丰富程度取决于Ingress Controller 的选用 |
HTTP host, path (with full regular expression support), method, headers, ports, query parameters, and more. |
| 实现原理 | kube-proxy+iptables | nginx-ingress+kube-proxy+iptables | |
| 其它特性 | retried, injecting faults or delays for testing, and rewriting or redirecting requests. |
以下 是一个通过ingress 访问 pod 的示例
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: web
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: website-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: nginx-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- website-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: nginx-service
subset: subset1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: nginx-destination-rule
spec:
host: nginx-service
subsets:
- name: subset1
labels:
app: web
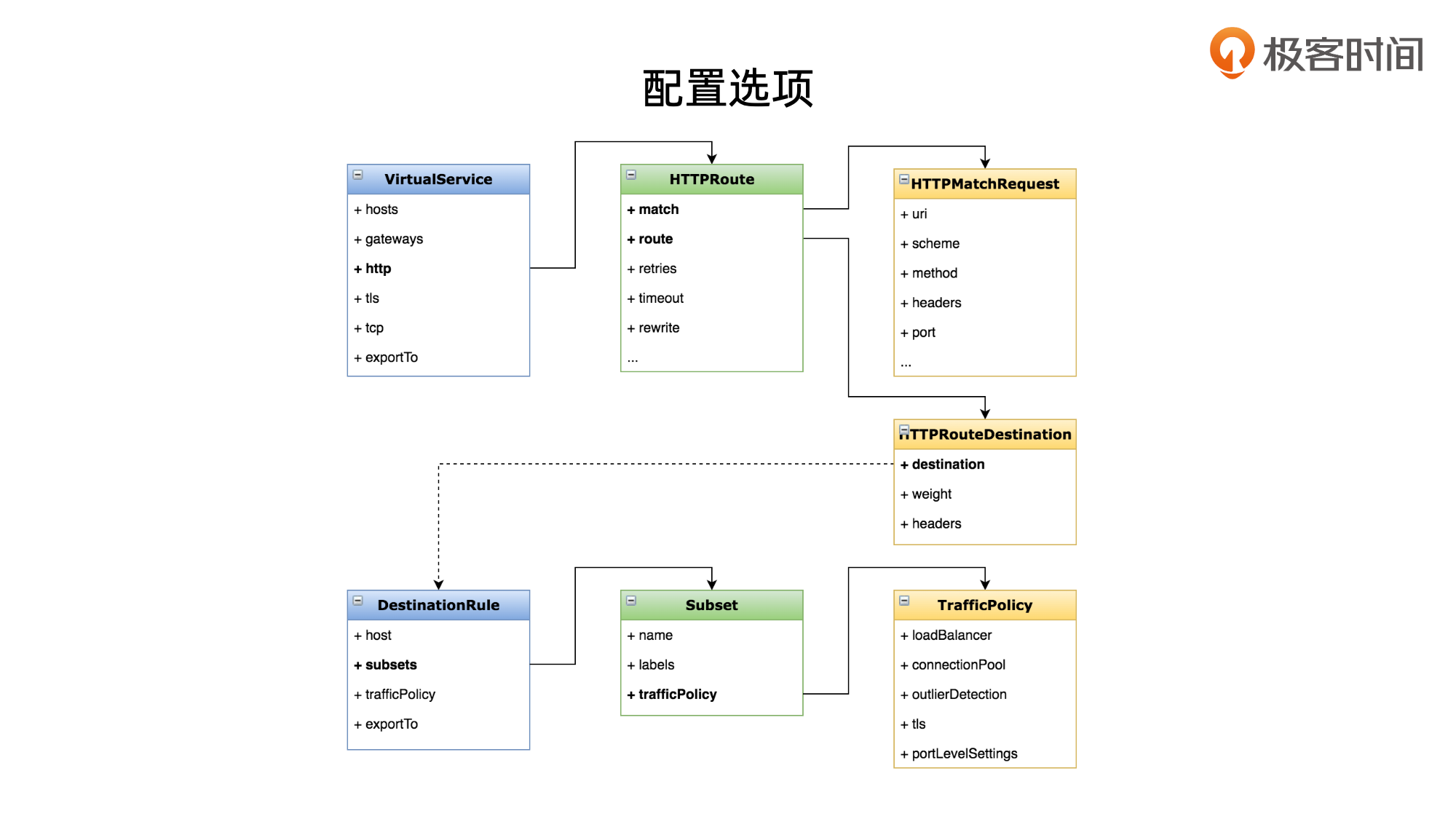
- istio 只是指定了 流量入口,具体的 路由工作由 绑定的VirtualService 负责
- VirtualService 负责配置路由规则 match,demo 中为简单起见没有配置,表示所有流量都路由到 http.route 指定的destination(也就是一个service)
相关组件
与istio ingress 功能对应的 是istio-ingressgateway Pod 以及附属的 istio-ingressgateway Service
root@ubuntu-01:~# kubectl describe pod istio-ingressgateway-74cb7595bd-gqhl7 -n istio-system
Name: istio-ingressgateway-74cb7595bd-gqhl7
Namespace: istio-system
Priority: 0
Node: ubuntu-02/192.168.56.102
Start Time: Wed, 27 May 2020 18:01:36 +0800
Labels: app=istio-ingressgateway
chart=gateways
heritage=Tiller
istio=ingressgateway
pod-template-hash=74cb7595bd
release=istio
service.istio.io/canonical-name=istio-ingressgateway
service.istio.io/canonical-revision=latest
Annotations: sidecar.istio.io/inject: false
root@ubuntu-01:~# kubectl describe svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
Name: istio-ingressgateway
Namespace: istio-system
Labels: app=istio-ingressgateway
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource=installed-state
istio=ingressgateway
operator.istio.io/component=IngressGateways
operator.istio.io/managed=Reconcile
operator.istio.io/version=1.6.0
release=istio
Annotations: Selector: app=istio-ingressgateway,istio=ingressgateway
Type: LoadBalancer
- istio-ingressgateway Pod 运行了一个envoy ,从istio 中接收 xds 数据
- istio-ingressgateway 是一个 LoadBalancer 类型的 Service,通过NodePort 转发数据。包含一个Label
istio: ingressgateway与 istio Gateway 的selector 相对应
root@ubuntu-01:~# kubectl exec -it istio-ingressgateway-74cb7595bd-gqhl7 -n istio-system bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
root@istio-ingressgateway-74cb7595bd-gqhl7:/# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 02:02 ? 00:00:10 /usr/local/bin/pilot-agent proxy router --domain istio-system.svc.cluster.local --proxyLogLevel=warning --proxyCom
root 13 1 0 02:02 ? 00:01:13 /usr/local/bin/envoy -c etc/istio/proxy/envoy-rev0.json --restart-epoch 0 --drain-time-s 45 --parent-shutdown-time
root 27 0 0 05:48 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
请求包流转
curl http://node-ip:istio-ingressgateway-service-node-port请求发往 istio-ingressgateway Service- 通过iptables,流量被转发到 istio-ingressgateway Pod
- 进入pod 查看envoy实时配置
curl http://127.0.0.1:15000/config_dump /path 下的流量被转发到outbound_.80_._.nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local对应的 k8s serviceoutbound|80||nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local- 深入解读Service Mesh背后的技术细节pilot使用Kubernetes的Service,仅仅使用它的服务发现功能,而不使用它的转发功能,pilot通过在kubernetes里面注册一个controller来监听事件,从而获取Service和Kubernetes的Endpoint以及Pod的关系,但是在转发层面,就不会再使用kube-proxy根据service下发的iptables规则进行转发了,而是将这些映射关系转换成为pilot自己的转发模型,下发到envoy进行转发,这样就把控制面和数据面彻底分离开来,服务之间的相互关系是管理面的事情,不要和真正的转发绑定在一起。
{
"configs":[
{
"static_clusters": [],
"dynamic_active_clusters":[]
}
{
"static_route_configs": [],
"dynamic_route_configs": [
{
"route_config":{
"virtual_hosts":[
{
"routes":[]
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
// dynamic_active_clusters 中跟demo 相关的部分
{
"version_info": "2020-05-30T06:02:33Z/24",
"cluster": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.api.v2.Cluster",
"name": "outbound|80||nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
"type": "EDS",
"eds_cluster_config": {
"eds_config": {
"ads": {}
},
"service_name": "outbound|80||nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local"
},
"connect_timeout": "10s",
"circuit_breakers": {},
"metadata": {},
"filters": [],
"transport_socket_matches": []
},
"last_updated": "2020-05-30T06:02:34.248Z"
},
// routes 中 跟 demo 相关的部分
{
"match": {
"prefix": "/"
},
"route": {
"cluster": "outbound|80|subset1|nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
"timeout": "0s",
"retry_policy": {},
"max_grpc_timeout": "0s"
},
"metadata": {
"filter_metadata": {
"istio": {
"config": "/apis/networking.istio.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/default/virtual-service/nginx-virtual-service"
}
}
},
"decorator": {
"operation": "nginx-service.default.svc.cluster.local:80/*"
}
}
