前言
- 一个或多个Acceptor线程,每个线程都有自己的Selector,Acceptor只负责accept新的连接,一旦连接建立之后就将连接注册到其他Worker线程中
- 多个Worker线程,有时候也叫IO线程,就是专门负责IO读写的。
- 一种实现方式就是像Netty一样,每个Worker线程都有自己的Selector,可以负责多个连接的IO读写事件,每个连接归属于某个线程。
- 一种方式实现方式就是有专门的线程负责IO事件监听,这些线程有自己的Selector,一旦监听到有IO读写事件,并不是像第一种实现方式那样(自己去执行IO操作),而是将IO操作封装成一个Runnable交给Worker线程池来执行,这种情况每个连接可能会被多个线程同时操作,相比第一种并发性提高了,但是也可能引来多线程问题,在处理上要更加谨慎些。tomcat的NIO模型就是第二种。
java nio 介绍
java nio类库的三个基本组件bytebuffer,channel,selector, 它们是spi接口,java并不提供详细的实现(由jvm提供),java只是将这三个组件赤裸裸的提供给你,线程模型由我们自己决定采用,数据协议由我们自己制定并解析。
首先我们要了解java nio原生的类体系。以Channel interface为例,Channel,InterruptibleChannel,SelectableChannel等interface逐步扩展了Channel的特性。java源码中channel的注释:A nexus(连结、连系) for I/O operations。
Java NIO TutorialIn the standard IO API you work with byte streams and character streams. In NIO you work with channels and buffers. Data is always read from a channel into a buffer, or written from a buffer to a channel.
public interface Channel extends Closeable {
public boolean isOpen();
public void close() throws IOException;
}
// 并没有新增方法,只是说明,实现这个接口的类,要支持Interruptible特性。
public interface InterruptibleChannel
extends Channel
public void close() throws IOException;
}
A channel that can be asynchronously closed and interrupted. A channel that implements this interface is asynchronously closeable: If a thread is blocked in an I/O operation on an interruptible channel then another thread may invoke the channel’s close method. This will cause the blocked thread to receive an AsynchronousCloseException.
这就解释了,好多类携带Interruptible的含义。
public abstract class SelectableChannel extends AbstractInterruptibleChannel implements Channel{
// SelectorProvider,Service-provider class for selectors and selectable channels.
public abstract SelectorProvider provider();
public abstract int validOps();
public abstract boolean isRegistered();
public abstract SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att)
throws ClosedChannelException;
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops)
throws ClosedChannelException{
return register(sel, ops, null);
}
public abstract SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block)
throws IOException;
public abstract boolean isBlocking();
public abstract Object blockingLock();
}
In order to be used with a selector, an instance of this class must first be registered via the register method. This method returns a new SelectionKey object that represents the channel’s registration with the selector.
通过以上接口定义,我们可以知道,Channel接口定义的比较宽泛,理论上bio也可以实现Channel接口。所以,我们在分析selector和Channel的关系时,准确的说是分析selector与selectableChannel的关系:它们是相互引用的。selector和selectableChannel是多对多的关系,数据库中表示多对多关系,需要一个中间表。面向对象表示多对多关系则需要一个中间对象,SelectionKey。selector和selectableChannel都持有这个selectionkey集合。
线程模型
从最简单的代码开始,逐步拆解,演示下如何在nio编程中应用各种线程模型。网络 IO 演变发展过程和模型介绍
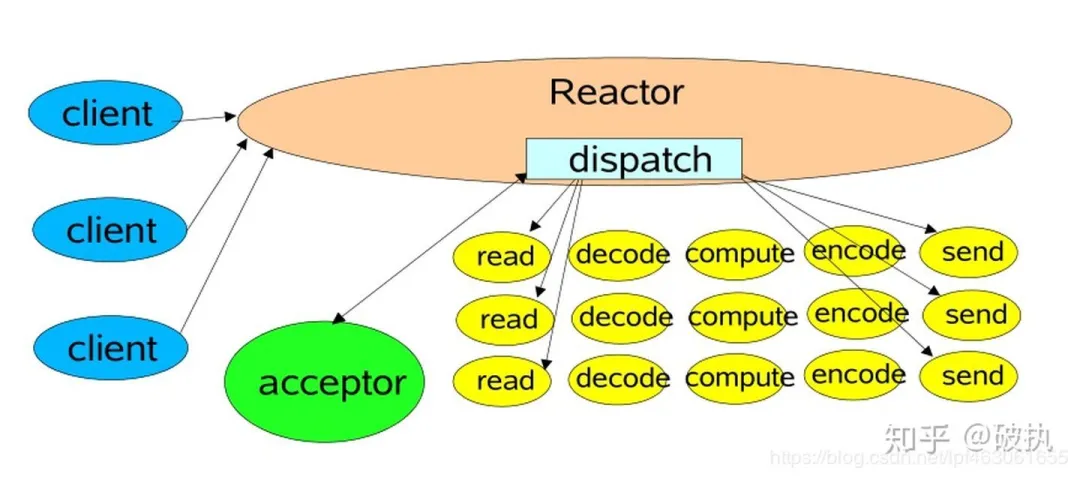
单 reactor 单线程模型
只有一个 epoll 对象(体现在java 上就是Selector),所有的接收客户端连接、客户端读取、客户端写入操作都包含在一个线程内。该种模型也有一些中间件在用,比如 redis。
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleKey(key);
}
}
}
public static void handleKey(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// Accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
// Add the new connection to the selector
sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("accept...");
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// handle buffer
int count = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (count > 0) {
String receiveText = new String(readBuffer.array(), 0, count);
System.out.println("服务器端接受客户端数据--:" + receiveText);
}
}
}
}
代码中,while(true){监听并处理事件}循环有个学名,叫eventloop。
while(ture){
// 阻塞
selectKeys = select();
// 非阻塞
handleKey(selectKeys);
}
在该示例中,所有工作放在一个线程中处理,很明显可靠性较低且性能不高。
- 从事件属性上讲,包括:accept事件、read/write事件。
- 从任务属性上讲,包括io任务(r/w data),read/write数据的处理(对data的业务处理)等
| 事件 | 任务(处理事件) | |
|---|---|---|
| accept | 新连接进来 | 将新连接的socket注册到selector |
| read | 读缓冲区有数据 | 数据解码、进行业务处理 |
| write | 写缓冲区有空闲 | 数据编码,写入socket send buffer |
单 reactor 多线程模型——io线程和业务线程分开
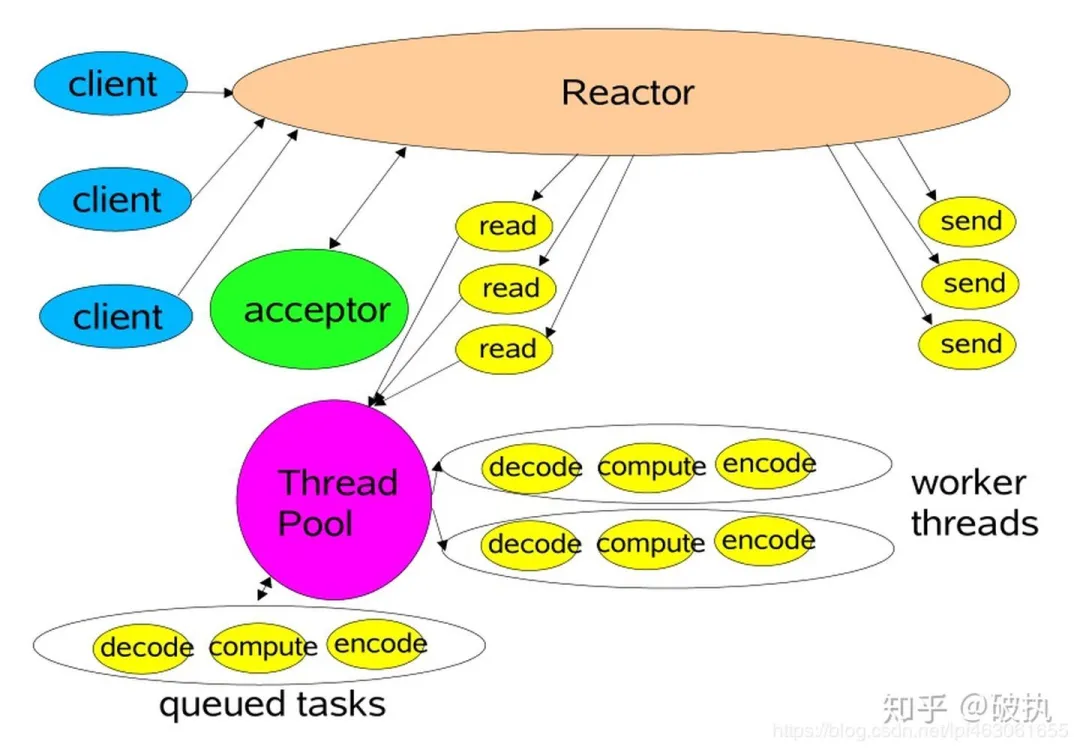
最容易想到的办法,当数据readable时,启动线程池,开启一个新的任务专门处理该数据,高大上点说就是:io线程和业务线程分开,因此上节的handlerKey方法简化成了。
public static void handleKey(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// Accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
// Add the new connection to the selector
sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("accept...");
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
executor.execute(new Reader(key));
}
}
对应的,红色部分交给线程池处理
| 事件 | 任务(处理事件) | |
|---|---|---|
| accept | 新连接进来 | 将新连接的socket注册到selector |
| read | 读缓冲区有数据 | 数据解码、进行业务处理 |
| write | 写缓冲区有空闲 | 数据编码,写入socket send buffer |
multi-reactor 多线程模型——io线程按事件类型分开
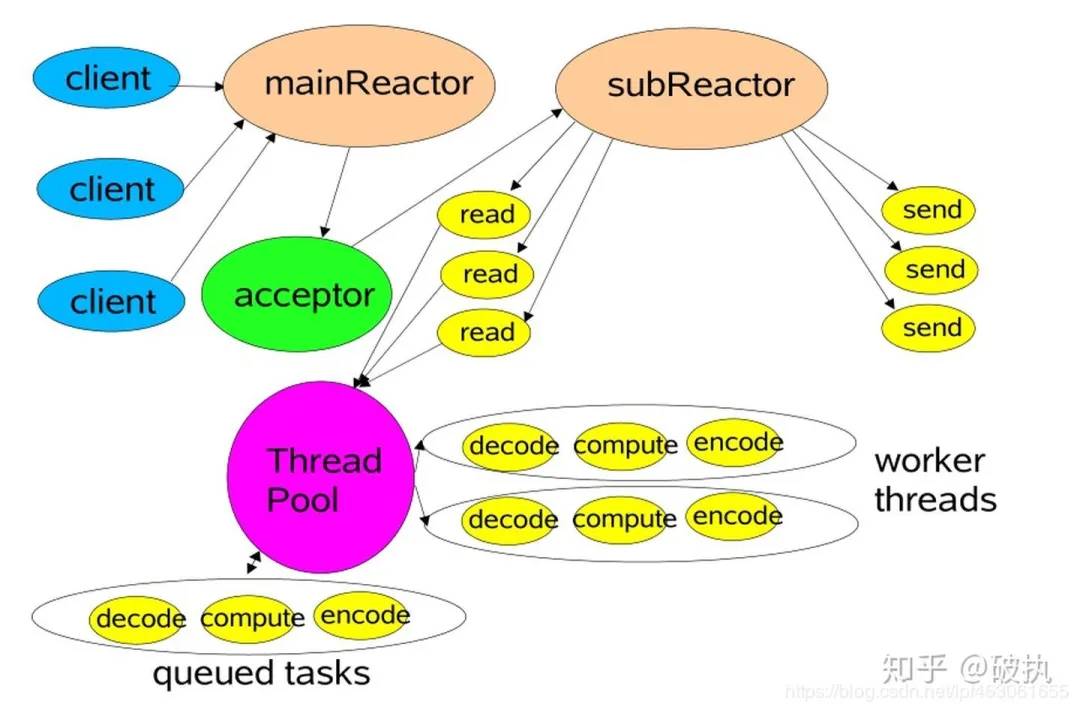
主要分为两个部分:mainReactor、subReactors。mainReactor 主要负责接收客户端的连接,然后将建立的客户端连接通过负载均衡的方式分发给 subReactors,subReactors 来负责具体的每个连接的读写。对于非 IO 的操作,依然交给工作线程池去做,对逻辑进行解耦
public class NIOServer {
private static ExecutorService boosExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
private static ExecutorService workerExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
private static Queue<SocketChannel> workerQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<SocketChannel>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* boss只处理连接事件,worker只处理读写事件。
* 将两者分开的关键就是使用两个selector
*/
Selector bossSelector = Selector.open();
Selector workerSelector = Selector.open();
Boss boss = new Boss(bossSelector,workerQueue);
boss.bind();
boosExecutor.execute(boss);
workerExecutor.execute(new Worker(workerSelector,workerQueue));
}
}
boss线程实现
public class Boss implements Runnable {
public void bind() throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleKey(key);
}
}
}
private void handleKey(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// Accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
System.out.println("boss connect...");
// 向woker队列中发送建立连接的SocketChannel
workerQueue.add(sc);
System.out.println("boss queue size " + workerQueue.size());
}
}
}
worker线程实现
public class Worker implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while (true) {
process(workerQueue);
process(selector);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
public void process(Queue<SocketChannel> queue) throws IOException{
// 如果队列为空,会返回null,不会阻塞
SocketChannel sc = workerQueue.poll();
if(null != sc){
System.out.println("worker accept ...");
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
public void process(Selector selector) throws IOException{
//此处必须设置超时,因为最开始worker的selector没有绑定SocketChannel,所以“selector.select()会阻塞,并且再也无法恢复”
selector.select(1000);
// 处理读写事件
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleKey(key);
}
}
}
对应的,蓝色部分由boss线程(group)负责,红色部分由worker线程(group)负责。
| 事件 | 任务(处理事件) | |
|---|---|---|
| accept | 新连接进来 | 将新连接的socket注册到selector |
| read | 读缓冲区有数据 | 数据解码、进行业务处理 |
| write | 写缓冲区有空闲 | 数据编码,写入socket send buffer |
io线程与selector 绑定
io 线程的分化是随着 selector 功能的分化进行的,每个io线程都会聚合一个selector
XXthread{
private Selector selector
public void run(){
while(true){
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
...
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
...
}
}
}
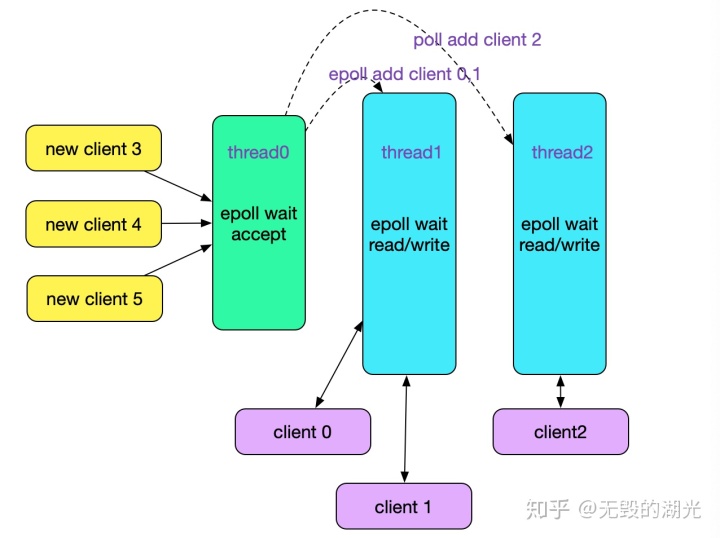
kafka 中 专门负责acceptable事件 线程称为 acceptor thread, 负责readable/writable事件的称为 processor thread。netty 中都称为 eventloop,但在使用时命名有所区分,前者称之为boss,后者称之为worker。netty的处理方式也体现了,“io线程与业务线程分化” 与 “io线程本身的分化” 有一点不同:后者虽然分化了,但不同线程整体的处理逻辑是一致的。就好比一些rpc 框架支持快慢线程池的功能,快慢线程池中不同线程的处理逻辑是一样的,只是为了优先保证重要业务的可靠性才做的区分。
java 多线程编程中,一般推荐将自己的逻辑封装为Runnable提交给线程池。但在很多框架的实现中,通常会将 thread 和 相关数据封装一下 对外提供系统的操作对象,这类对象通常不聚合thread 对象也没有什么问题。按照“程序=控制+逻辑”的公式,此时的线程只是一个“控制”方式,并不影响 封装对象对外提供的 逻辑接口,我们从 reactor 模式的概念图中也没找到 thread的影子不是。
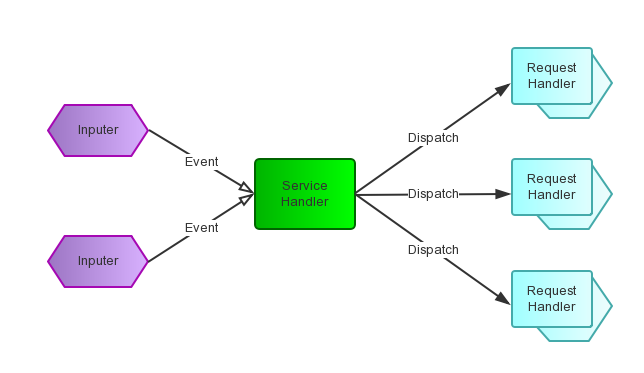
io线程和业务线程的数据交互
在netty 中,io线程读取到数据后,可以直接操作线程池对象来执行 业务处理逻辑。kafka 则在io 线程与业务线程之间 提供了一个队列来缓冲数据,Processor thread 将读取的数据放入 RequestChannel(对队列的封装),Handler thread读取 并将处理后的响应通过 RequestChannel 传递给Processor。 Handler thread 属于kafka的 API层。
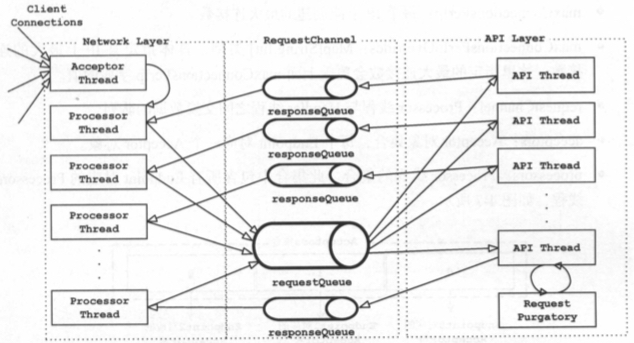
一般来说服务端程序有几个角色:Acceptor、Selector 和 Processor。
- Acceptor 负责接收新连接,也就是 accept;
- Selector 负责检测连接上的 I/O 事件,也就是 select;
- Processor 负责数据读写、编解码和业务处理,也就是 read、decode、process、encode、send。
Acceptor 在接收连接时,可能会阻塞,为了不耽误其他工作,一般跑在单独的线程里;而 Selector 在侦测 I/O 事件时也可能阻塞,但是它一次可以检测多个 Channel(连接),其实就是用阻塞它一个来换取大量业务线程的不阻塞,那 Selector 检测 I/O 事件到了,是用同一个线程来执行 Processor,还是另一个线程来执行呢?不同的场景又有相应的策略。
比如 Netty 通过 EventLoop 将 Selector 和 Processor 跑在同一个线程。一个 EventLoop 绑定了一个线程,并且持有一个 Selector。而 Processor 的处理过程被封装成一个个任务,一个 EventLoop 负责处理多个 Channel 上的所有任务,而一个 Channel 只能由一个 EventLoop 来处理,这就保证了任务执行的线程安全,并且用同一个线程来侦测 I/O 事件和读写数据,可以充分利用 CPU 缓存。请你注意,这要求 Processor 中的任务能在短时间完成,否则会阻塞这个 EventLoop 上其他 Channel 的处理。因此在 Netty 中,可以设置业务处理和 I/O 处理的时间比率,超过这个比率则将任务扔到专门的业务线程池来执行,这一点跟 Jetty 的 EatWhatYouKill 线程策略有异曲同工之妙。
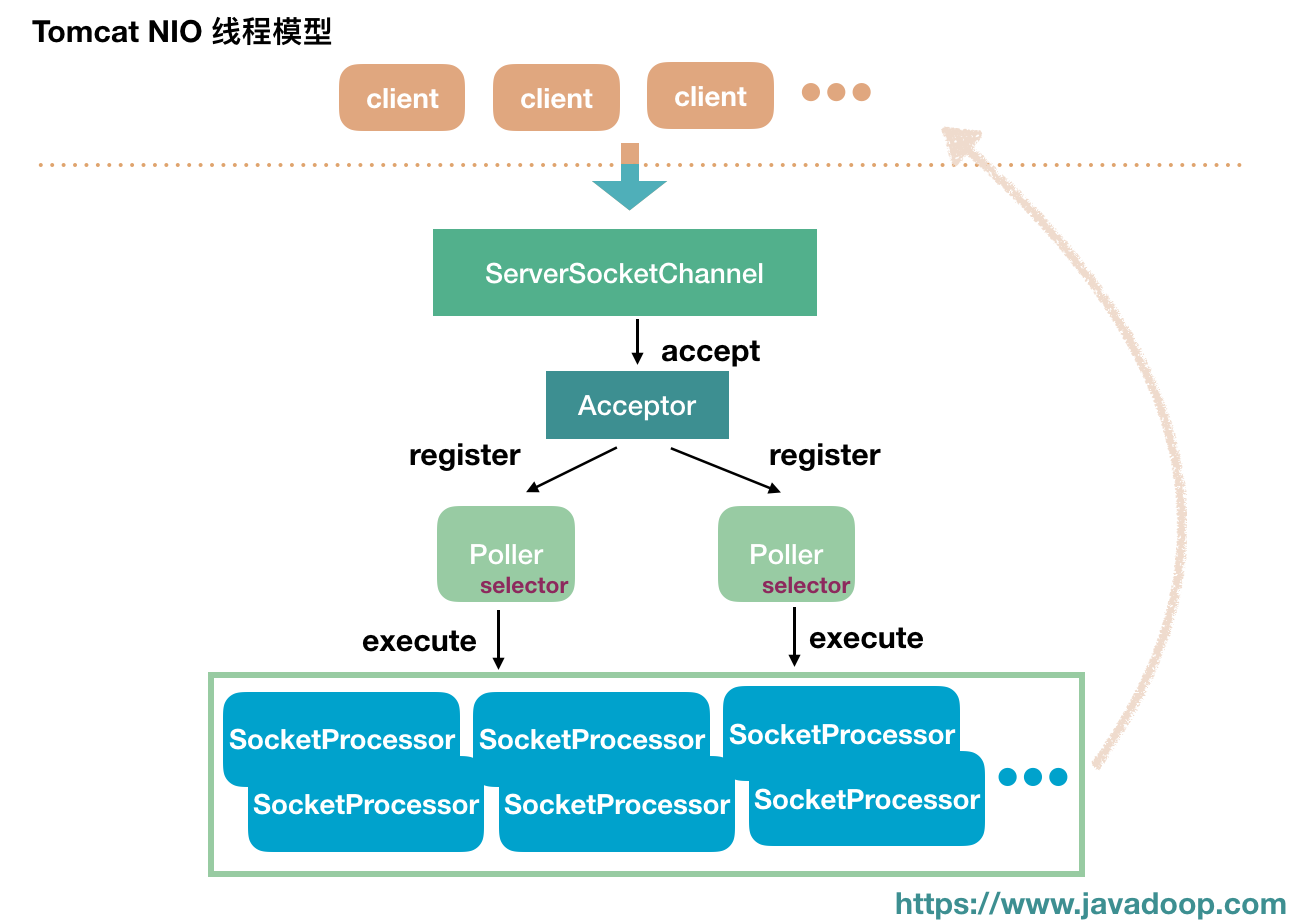
而 Kafka 把 Selector 和 Processor 跑在不同的线程里,因为 Kafka 的业务逻辑大多涉及与磁盘读写,处理时间不确定,所以 Kafka 有专门的业务处理线程池来运行 Processor。与此类似,Tomcat 也采用了这样的策略
NIO的使用套路
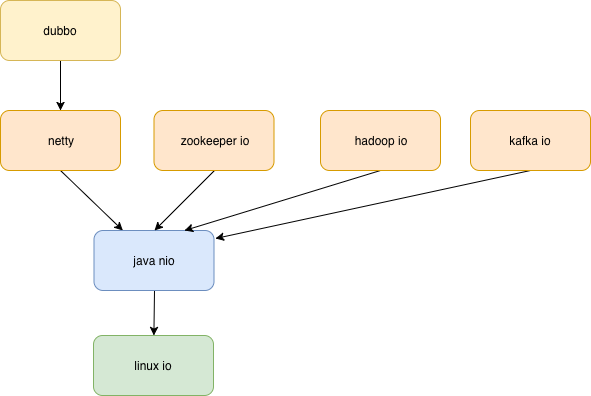
在具体实践中,各个框架套路不一样
- hadoop,Thread-Per-Connection,与BIO的思路一样,只是用了NIO的API
- kafka客户端,一个线程 一个selector 裸调java NIO 进行网络通信
- netty和kafka 服务端都采用主从线程模型,但在io线程和业务线程的交互上有差异,如上文所述