简介
谈一谈企业级弹性伸缩与优化建设 系统的讲了弹性能力平台化。
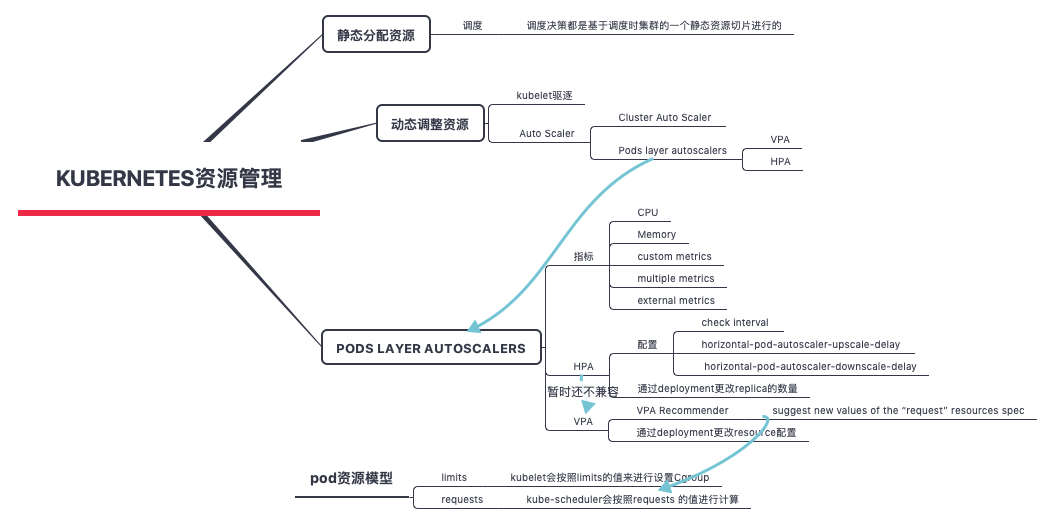
Kubernetes at its core is a resources management and orchestration tool. It is ok to focus day-1 operations to explore and play around with its cool features to deploy, monitor and control your pods. However, you need to think of day-2 operations as well. You need to focus on questions like:
- How am I going to scale pods and applications?
- How can I keep containers running in a healthy state and running efficiently?
- With the on-going changes in my code and my users’ workloads, how can I keep up with such changes?
- 激增的流量负载与资源容量规划的矛盾如何解决?资源成本与系统可用性如何平衡?
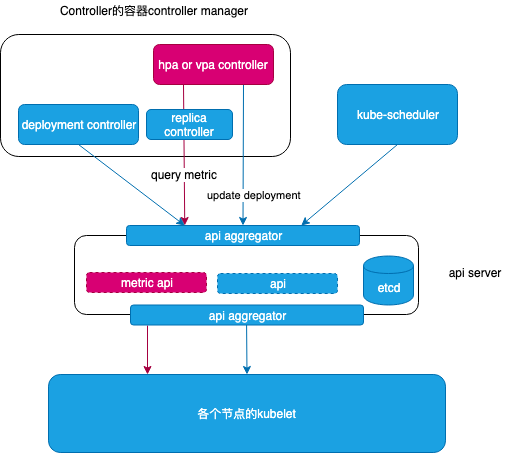
HPA和VPA工作原理——CRD的典型应用
-
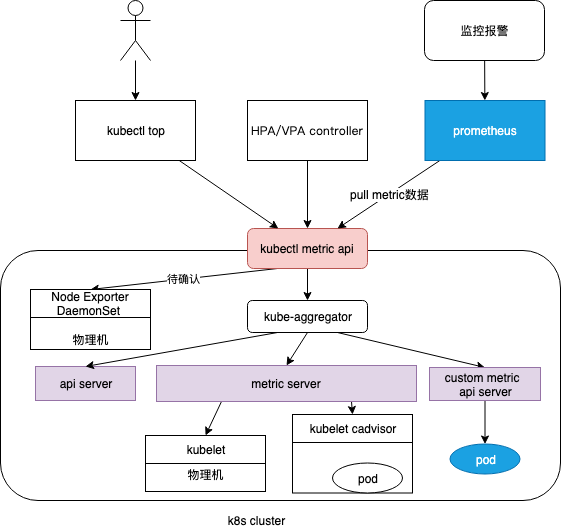
hpa 和 vpa 做出决策依赖 metric server 提供的metric 数据
- Kubernetes 本身“安装” hpa 和 vpa 的CRD,以支持vpa or hpa Kubernetes object
- 对于每个应用,创建一个对象的vpa or hpa对象
- hpa or vpa CRD 不停的拉取metric 数据,根据hpa or vpa 对象配置的策略,计算出pod 的最佳replica(hpa)或resource(vpa),更改deployment 配置,重启deployment
Vertical Pod Autoscaler
Kubernetes 垂直自动伸缩走向何方?垂直自动伸缩(VPA,Vertical Pod Autoscaler) 是一个基于历史数据、集群可使用资源数量和实时的事件(如 OMM, 即 out of memory)来自动设置Pod所需资源并且能够在运行时自动调整资源基础服务。
K8s降本增效之VPA上篇 值得看一下。
B站容器云平台VPA技术实践 VPA一般需要具备以下三种关键能力:
- 容器资源规格推荐。基于应用的真实负载,根据特定的算法计算出容器的合理资源规格。
- 对于新创建的Pod,需要基于k8s webhook,在创建Pod对象的过程中将资源规格修改为推荐值。
- 对于已经创建的Pod,需要定时动态调整容器的资源规格。很多业务不希望VPA调整资源配额时发生pod驱逐,因此业界也有部分公司选择修改K8S源代码来支持in-place VPA的能力,从而实现动态修改容器资源规格。K8S社区对于 in-place VPA已经有相关issue讨论。
示例
配置示例
apiVersion: autoscaling.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: my-rec-vpa
spec:
targetRef:
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
kind: Deployment
name: my-rec-deployment
updatePolicy:
updateMode: "Off"
- targetRef 指定了被监控的对象是名叫 my-rec-deployment的Deployment
kubectl create -f my-rec-vpa.yaml稍等片刻,然后查看 VerticalPodAutoscaler:kubectl get vpa my-rec-vpa --output yaml
输出结果显示推荐的 CPU 和内存请求:
recommendation:
containerRecommendations:
- containerName: my-rec-container
lowerBound:
cpu: 25m
memory: 262144k
target:
cpu: 25m
memory: 262144k
upperBound:
cpu: 7931m
memory: 8291500k
target 推荐显示,容器请求25 milliCPU 和 262144 千字节的内存时将以最佳状态运行。
配置示例
apiVersion: autoscaling.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: my-vpa
spec:
targetRef:
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
kind: Deployment
name: my-deployment
updatePolicy:
updateMode: "Auto"
- targetRef 指定了被监控的对象是名叫 my-deployment的Deployment
- updateMode 字段的值为 Auto,意味着VerticalPodAutoscaler 可以删除 Pod,调整 CPU 和内存请求,然后启动一个新 Pod。
- VerticalPodAutoscaler 使用 lowerBound 和 upperBound 推荐值来决定是否删除 Pod 并将其替换为新 Pod。如果 Pod 的请求小于下限或大于上限,则 VerticalPodAutoscaler 将删除 Pod 并将其替换为具有目标推荐值的 Pod。
原理
综述:
- 提出新的API资源: VerticalPodAutoscaler 。它包括一个标签识别器 label selector(匹配Pod)、资源策略 resources policy(控制VPA如何计算资源)、更新策略 update policy(控制资源变化应用到Pod)和推荐资源信息。
- VPA Recommender 是一个新的组件,它考虑集群中来自 Metrics Server 的所有 Pod 的资源利用率信号和内存溢出事件。
- VPA Recommender 会监控所有 Pod,为每个 Pod 持续计算新的推荐资源,并将它们存储到 VPA Object 中。
- VPA Recommender 会暴露一个同步 API 获取 Pod 详细信息并返回推荐信息。
- 所有的 Pod 创建请求都会通过 VPA Admission Controller。如果 Pod 与任何一个 VPA 对象匹配,那么 Admission controller 会依据 VPA Recommender 推荐的值重写容器的资源。如果 Recommender 连接不上,它将会返回 VPA Object 中缓存的推荐信息。
- VPA Updater 是负责实时更新 Pod 的组件。如果一个 Pod 使用 VPA 的自动模式,那么 Updater 会依据推荐资源来决定如何更新。在 MVP 模式中,这需要通过删除 Pod 然后依据新的资源重建 Pod 来实现,这种方法需要 Pod 属于一个 Replica Set(或者其他能够重新创建它的组件)。在未来,Updater 会利用原地升级,因为重新创建或者重新分配Pod对服务是很有破坏性的,必须尽量减少这种操作。
- VPA 仅仅控制容器的资源请求,它把资源限制设置为无限,资源请求的计算基于对当前和过去运行状况的分析。
- History Storage 是从 API Server 中获取资源利用率信号和内存溢出并将它们永久保存的组件。Recommender 在一开始用这些历史数据来初始化状态。History Storage 基础的实现是使用 Prometheus。
updatePolicy
- Intitial: VPA 只在创建 Pod 时分配资源,在 Pod 的其他生命周期不改变Pod的资源。
- Auto(默认):VPA 在 Pod 创建时分配资源,并且能够在 Pod 的其他生命周期更新它们,包括淘汰和重新调度 Pod。
- Off:VPA 从不改变Pod资源。Recommender 而依旧会在VPA对象中生成推荐信息,他们可以被用在演习中。 PS:K8s 1.33 支持原地扩缩容
实践
中国工商银行容器在线纵向扩容的创新实践目前最常用的策略是通过增加容器副本数来提升系统整体的处理能力,即容器横向扩容,但只适用于无状态服务,而对于一些有状态服务(如数据库服务、消息队列等中间件应用)并不适用。大型互联网公司(如亚马逊、谷歌、IBM 等)均在容器纵向扩容领域开展了较多实践(如表 1 所示)。容器纵向扩容的主要实现方式有两种:Vertical Pod Autoscaler(VPA)方式和修改 Kubernetes 源码方式。其中,VPA 方式能够根据容器资源使用率自动设置 CPU 和内存的软硬限制,从而为每个容器提供适当的资源,但需要重建容器。修改 Kubernetes 源码方式可以保证容器在线扩容,但对 Kubernetes 源码侵入性较强,对于后续 Kubernetes 版本升级有较大影响。容器不重启修改容器资源的方式,PS: 感觉动静有点大。
- 更新容器的 cgroup,涉及到kubelet 四层的 CGroup 树 结构
- 取出 ETCD 中 PodSpec 数据,修改完限制参数再更新至 ETCD。
- 重新计算 PodSpec 的 Hash 值,将最新的 Hash 值更新至 PodSpec。只要 v1.Container 的任何一个字段发生改变都会导致期望的容器 hash 值变化。如果 hash 值变化则返回 true, Kubelet就会执行 SyncPod 方法重启Pod。
唯品会有提过一个通过docker api 直接改容器资源的方案,也无需重启容器。
Pod 垂直自动伸缩的使用 vpa局限性
- 不能和 HPA 一起使用
- 需要至少两个健康的 Pod 才能工作。由于 VPA 会破坏一个 Pod,并重新创建一个 Pod 来进行垂直自动伸缩,因此它需要至少两个监控的 Pod 副本来确保不会出现服务中断。
- 默认最小内存分配为250MiB
- 不能用于单个独立的 Pod。VPA 只适用于 Deployments、StatefulSets、DaemonSets、ReplicaSets 等控制器
目前 VPA 在生产中的最佳方式是在推荐模式下使用,这有助于我们了解最佳的资源请求值是多少,以及随着时间推移它们是如何变化的。 一旦配置了,我们就可以通过获取这些 metrics 指标,并将其发送到监控工具中去,比如 Prometheus 和 Grafana 或者 ELK 技术栈。然后可以利用这些数据来调整 Pods 的大小。
Pod 原地垂直伸缩 - 一个四年的KEP和两年的PR 讲了具体实现和原理,值得细读。
Cluster Auto Scaler
Airbnb 如何实现 Kubernetes 集群动态扩展 提到了对CA的扩展。 kubernetes 资源管理概述
应用层的自动伸缩负责对 Pods 的自动伸缩控制。设想一个场景,某个服务在突增的业务高峰需要 100 个 Pods 扛住流量,集群常备的资源够跑 50 个Pods,那会剩余 50 个 Pods 没有资源可以调度。这个就是资源层弹性要解决的问题了,资源层弹性负责集群有足够的资源调度 Pods,且在不需要那么多资源的时候,自动释放,不造成太大的浪费。
随着业务的发展,应用会逐渐增多,每个应用使用的资源也会增加,总会出现集群资源不足的情况。为了动态地应对这一状况,我们还需要 CLuster Auto Scaler,能够根据整个集群的资源使用情况来增减节点。CA 是面向事件工作的,并每 10 秒检查一次是否存在不可调度(Pending)的 Pod(当调度器无法找到可以容纳 Pod 的节点时,这个 Pod 是不可调度的)。此时,CA 开始创建新节点。
CA( cluster-autoscaler)是用来弹性伸缩kubernetes集群的,自动的根据部署的应用所请求的资源量来动态的伸缩集群
- 什么时候扩?
- 由于资源不足,pod调度失败,导致pod处于pending状态时。
- 什么时候缩? node的资源利用率较低时,且此node上存在的pod都能被重新调度到其他节点
- 什么样的节点不会被CA删除
- 节点上有pod被PodDisruptionBudget控制器限制。
- 节点上有命名空间是kube-system的pods。
- 节点上的pod不是被控制器创建,例如不是被deployment, replica set, job, stateful set创建。
- 节点上有pod使用了本地存储
- 节点上pod驱逐后无处可去,即没有其他node能调度这个pod
- 节点有注解:”cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled”: “true”
- 如何防止node被Cluster Autoscaler删除
- kubectl annotate node cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled=true
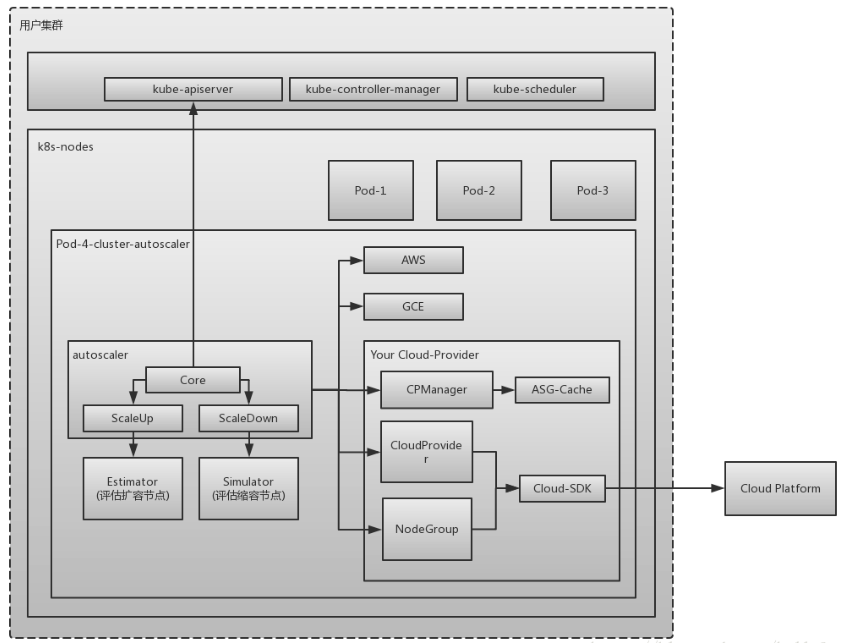
对于公有云来说,Cluster Auto Scaler 就是监控这个集群因为资源不足而 pending 的 pod,根据用户配置的阈值调用公有云的接口来申请创建机器或者销毁机器。对于私有云,则需要对接内部的管理平台。
源码分析
// k8s.io/autoscaler/cluster-autoscaler/core/static_autoscaler.go
// RunOnce iterates over node groups and scales them up/down if necessary
func (a *StaticAutoscaler) RunOnce(currentTime time.Time) errors.AutoscalerError {
...
unschedulablePods, err := unschedulablePodLister.List()
...
// 过滤掉实际可以调度的pod,实现上 拿候选node 都试一遍能不能跑在这些node上
unschedulablePodsToHelp, _ := a.processors.PodListProcessor.Process(a.AutoscalingContext, unschedulablePods)
if len(unschedulablePodsToHelp) == 0 {
scaleUpStatus.Result = status.ScaleUpNotNeeded
klog.V(1).Info("No unschedulable pods")
} else if a.MaxNodesTotal > 0 && len(readyNodes) >= a.MaxNodesTotal {
scaleUpStatus.Result = status.ScaleUpNoOptionsAvailable
klog.V(1).Info("Max total nodes in cluster reached")
} else if allPodsAreNew(unschedulablePodsToHelp, currentTime) {
a.processorCallbacks.DisableScaleDownForLoop()
scaleUpStatus.Result = status.ScaleUpInCooldown
klog.V(1).Info("Unschedulable pods are very new, waiting one iteration for more")
} else {
scaleUpStatus, typedErr = ScaleUp(autoscalingContext, a.processors, a.clusterStateRegistry, unschedulablePodsToHelp, readyNodes, daemonsets, nodeInfosForGroups, a.ignoredTaints)
if a.processors != nil && a.processors.ScaleUpStatusProcessor != nil {
a.processors.ScaleUpStatusProcessor.Process(autoscalingContext, scaleUpStatus)
scaleUpStatusProcessorAlreadyCalled = true
}
}
if a.ScaleDownEnabled {
...
}
}
从源码看,一开始先获取所有pending的pod,之后过滤掉实际可以调度的pod(实现上 拿候选node 都试一遍能不能跑在这些node上)。一般这样的pod 会带有一个 FailedScheduling(all nodes are unavailable) 标记,即调度器考察了所有节点,都发现无法执行这个任务(代码上倒没有检查这个状态)。
// k8s.io/autoscaler/cluster-autoscaler/utils/kubernetes/listers.go
// NewUnschedulablePodInNamespaceLister returns a lister providing pods that failed to be scheduled in the given namespace.
func NewUnschedulablePodInNamespaceLister(kubeClient client.Interface, namespace string, stopchannel <-chan struct{}) PodLister {
// watch unscheduled pods
selector := fields.ParseSelectorOrDie("spec.nodeName==" + "" + ",status.phase!=" +
string(apiv1.PodSucceeded) + ",status.phase!=" + string(apiv1.PodFailed))
podListWatch := cache.NewListWatchFromClient(kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient(), "pods", namespace, selector)
store, reflector := cache.NewNamespaceKeyedIndexerAndReflector(podListWatch, &apiv1.Pod{}, time.Hour)
podLister := v1lister.NewPodLister(store)
go reflector.Run(stopchannel)
return &UnschedulablePodLister{
podLister: podLister,
}
}
自定义crd 支持autoscaler
Scale subresource CustomResourceDefinition 需要在定义中支持 scale subresource
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: crontabs.stable.example.com
spec:
group: stable.example.com
versions:
- name: v1
served: true
storage: true
schema: ...
subresources:
# status enables the status subresource.
status: {}
# scale enables the scale subresource.
scale:
# specReplicasPath defines the JSONPath inside of a custom resource that corresponds to Scale.Spec.Replicas.
specReplicasPath: .spec.replicas
# statusReplicasPath defines the JSONPath inside of a custom resource that corresponds to Scale.Status.Replicas.
statusReplicasPath: .status.replicas
# labelSelectorPath defines the JSONPath inside of a custom resource that corresponds to Scale.Status.Selector.
labelSelectorPath: .status.labelSelector
scope: Namespaced
names:
plural: crontabs
singular: crontab
kind: CronTab
shortNames:
- ct
apply 带有subresource 的crd 之后, apiserver 提供api /apis/stable.example.com/v1/namespaces/*/crontabs/scale,也可以 通过 kubectl scale --replicas=5 crontabs/my-new-cron-object 命令来修改 CronTab.spec.replicas。
apiVersion: "stable.example.com/v1"
kind: CronTab
metadata:
name: my-new-cron-object
spec:
cronSpec: "* * * * */5"
image: my-awesome-cron-image
replicas: 3
可以直接修改 yaml CronTab.spec.replicas 来控制crd 的副本数,但无法与 hpa 等组件集成,hpa 使用rest api,无法直接 基于struct update apiserver,这样要依赖crd struct package。
其它
Kubernetes 垂直自动伸缩走向何方?通常用户在无状态的工作负载时选用 HPA,在有状态的工作负载时选用 VPA。
理论上 HPA 和 VPA 是可以共同工作的,HPA 负责瓶颈资源,VPA 负责其他资源。比如对于 CPU 密集型的应用,使用 HPA 监听 CPU 使用率来调整 pods 个数,然后用 VPA 监听其他资源(memory、IO)来动态扩展这些资源的 request 大小即可。当然这只是理想情况
